Introduction
The dark web, an intentionally hidden part of the internet, helps protect internet users’ privacy from traffic analysis attacks. This portion of the internet can only be accessed through specialized dark web browsers or technologies.
Manual research, which analysts widely use, is both time-consuming and ultimately inefficient. Some studies have used automated mechanisms to discover DarkWeb, but information about studies that systematically investigate or evaluate the content contained in its hidden network is scarce. This article highlights technological challenges when exploring illegal and extremist content using tools that can shed light on this anonymous network.
OSINT, or Open Source Intelligence, can scan to Decipher and find connections between criminals and other actors around them. Specialists can also use it to monitor information such as possible attacks and internal threats, as well as to neutralize or disrupt plans in real time.
Osint sources include newspapers, magazines, news, conferences, photographs, videos, social media accounts, blogs, press conferences, and academic documents. With the spread of the Internet and the increase in the use of social media, there has been a significant increase in OSINT sources. The point to be considered is collecting information from resources that do not require contact with the target. The combined and automated use of OSINT techniques allows a threat actor to reveal its name, location, IP address, or image.
In light of this information, we will try to convey a context to you in attempting to use OSINT techniques in a combined way in Darkweb research.
Introduction to the Dark Web
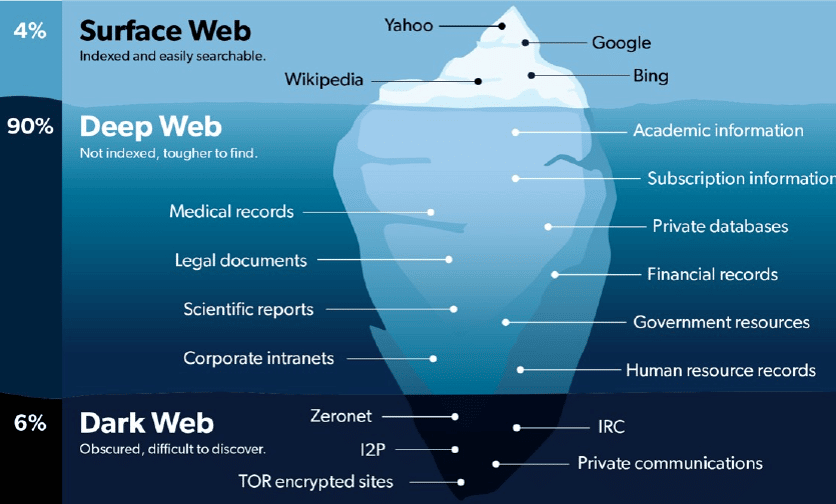
The deep web and the darknet are two very confused and very different concepts. The term “Deep Web” denotes a class of Internet content that, for various technical reasons, is not indexed by search engines.
Resources indexed by a search engine, whether or not a user goes to the site from the home page to ‘deeper’ to go, must have valid credentials such as a username and password. The part behind a page accessible by user verification in a media streaming service is considered part of the deep web because it is often blocked from accessing resources behind the home page of a search engine’s browser.
Sites where many authentication processes are required, such as email account contents, social media accounts, online banking accounts, and messaging application contents, constitute the deep web content. In addition, information such as legal documents, scientific research, academic studies, and databases of private institutions are also stored here.
The dark web is the worldwide web content contained in a private network: Overlay networks that use the internet but require specific software, configurations, or authorization to access it. Through the dark web, personal computer networks can communicate and conduct business anonymously without revealing identifying information, such as the user’s location. This also makes the dark web a subset of the bars we have on the Internet—websites on the Dark Web work in their unique environment, separated from the sites of surface sites. Cybercriminals use the dark web to coordinate and carry out cyberattacks, sell stolen data, and even exploit it to companies.
The dark network is often one of the issues that always maintain the mystery, with many misunderstandings. To take advantage of Darkweb, we need to analyze and correlate the data correctly. It can then become a valuable pool of information used in cyber security.
In this article, we will describe examples and scenarios through TOR, the most popular hidden network, when we talk about the dark web.
Why is the Dark Web So Important In Terms of Cyber Threat Intelligence?
The Dark web can be a valuable source of threat intelligence, where analysts can learn about how cyber attacks are carried out, stolen data, which attack tools are for sale and purchased, and the success rates of current cyber attack campaigns. However, this intelligence and creating a complete picture of the threat environment can be complex and requires a thorough understanding of the dark web and how to conduct an investigation.
Some threat information that analysts can find on the Dark Web include:
– Exposed Leaks, names, email addresses, and precision assets related to your organization are usually sold in dark web markets.
– Vulnerabilities are where security vulnerabilities in popular software used in many companies are sold.
– Threat Campaign, the necessary data can be accessed to track a new cyber attack campaign related to different sectors/scenarios.
– Digital Asset Accessing is sold, such as the database, critical servers, and infrastructures provided to sell infrastructure.
Following the dark web from a cybersecurity perspective gives us in-depth information about exciting monetization methods for criminals. By following these techniques and tactics, the next attack can be predicted and creates an essential context for us for pre-attack measures.
For these reasons, the dark web is an essential resource for OSINT because it makes up a large part of the internet and has rich content. Moreover, with dark web data collection, organizations or states can make discoveries about data breaches and illegal activities and take various measures accordingly. Here we will explain how data can be extracted via the dark web using OSINT techniques, how it can be analyzed, and the sample tools at the correlation point.
Why We Choose the TOR Hidden Network
Informally, the Dark Web refers to the small portion of the Deep Web (the part of the Web that is usually considered to be beyond reach from current search engines) based on darknets. Common darknets include, among other smaller P2P networks, FreeNet, the Invisible Internet Project (I2P), and Tor. In the case of Tor, Tor hidden services are used to access different applications such as chat, email, or websites through the Tor network.
In this article, we focus in particular on the analysis of websites hosted on Tor hidden services — due to Tor’s much more enormous popularity among users, which comprised around 7,000 relays or proxies by the time of this writing. The Tor network uses the onion routing technique for network traffic anonymization. Due to its nature, Tor hidden services are used for an extensive range of (cyber)-criminals activities. Thereby, several studies focused on how to discover, access, crawl, and categorize the content of the Dark Web.
Risks and Precautions When Using OSINT Tools on the Dark Web
The Dark Web presents unique challenges that require careful navigation. From malware and phishing attacks to misinformation and legal risks, exploring this hidden layer of the internet can be dangerous without proper precautions. Leveraging Brandefense’s solutions, including Dark Web Monitoring, Threat Intelligence, and Threat Detection, can help mitigate these risks effectively.
1. Malware
Malware is a prevalent risk on the Dark Web, often embedded in hidden websites or malicious files. Brandefense’s Dark Web Monitoring detects these threats in real-time, enabling organizations to act swiftly and prevent infections.
2. Phishing Attacks
Phishing campaigns on the Dark Web target unsuspecting users to steal credentials and sensitive data. With Brandefense’s Threat Intelligence, organizations can identify and neutralize phishing threats proactively.
3. Misinformation and Data Manipulation
Unverified or misleading information on the Dark Web can lead to inaccurate threat assessments. Brandefense’s Threat Detection ensures reliable and actionable intelligence, minimizing the risks of acting on false data.
4. Legal Challenges
Unintentional interaction with illegal activities on the Dark Web can lead to severe legal consequences. Brandefense provides tools to monitor and avoid these risks, ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards.
Dark Web Monitoring with OSINT
Although it is technically possible to create your dark web monitoring program, it is unrealistic. There are many platforms on the Dark web where personal information is sold or traded will require a high level of computational power and systematization, constantly scanning each of them. Knowing how to make the right business plan and solutions according to the problem is one of the challenging aspects of the job.
In this article, We will continue with a structure setup consisting of a simple methodology comprised of several steps and tools that you can successfully automate these steps.
These steps are mainly:
- How to get onion links over TOR
- How to search on these links
- How to collect the data through these connections
- How to process this data
Of course, the number of vehicles here can be increased, but we wanted to show you a few sample vehicles and for what purpose we use them to provide you with an overview from here. Over time, the tools may change, but the steps toward the goal will remain the same.
How to Get Onion Links Over TOR
Due to the TOR Network architecture, it is not easy to find relevant content because it is not suitable for the search engine structure used by central systems. Therefore, we try to solve this problem with some solutions close to the search engines we use in daily life.
As a first step, focus on deep-web search engines. The most popular are Ahmia.fi(http://ahmia.fi/) and The Uncensored Hidden Wiki, these two work with a different logic from each other.
Ahmia
Juha Nurmi developed Ahmia as part of the Tor Project, which is one of the closest things to a deep web search engine. Ahmia essentially collects .onion URLs from the Tor network and then feeds these pages to their index, provided they don’t contain a robots.txt file saying not to index them. In addition, Ahmia allows onion service operators to register their URLs, enabling them to be found. Through continuously collecting .onion URLs, Ahmia has created one of the most extensive indexes of the deep web.

Hidden Wiki
Uncensored Hidden Wiki works slightly differently. Anyone can register with an uncensored hidden Wiki; after that, everyone can edit connections in the database. The search engine works by calling the descriptions of the pages given in these links. “.onion” since domain names are changed very often, crowdsourcing links is one of the best ways to collect many valuable URLs and keep them up to date.

Quick Tips
The Hunchly Dark Web mailing list provides daily reports of hidden services on the Tor network. Combined with the other two alternatives in this list that can be taken daily, it can provide actionable intelligence findings.
How to Collect Data on These Links
TorBot
TorBot is a dark web OSINT tool. It is written in Python and is open source. Dark on the web .scans sites with the onion extension. Some features include:
- Returns Page title and address with a short description of the site.
- Save crawl info to JSON file
- Crawl custom domains.
- Checking if the link is live.
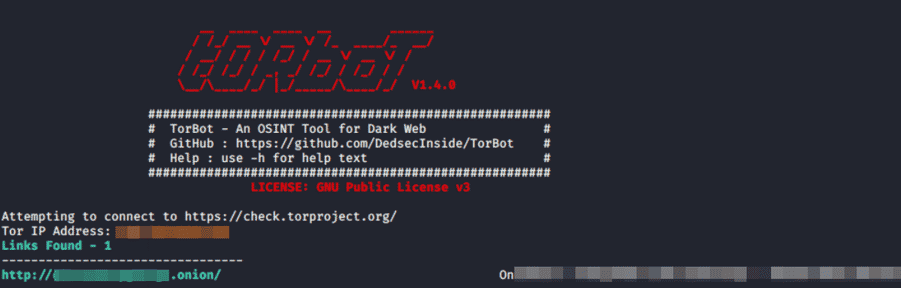
Due to these features, the TorBot tool turns out to be a tool that performs many tasks on its own with all the solutions we need. Information collection processes on the Dark web with OSINT can be easily performed using various tools. One of these tools, TorBot, is a valuable tool with ease of use and essential information that it gives as output. It is important to use similar tools to shorten the information collection process.
How to Process This Data
We manually collected Tor links and obtained other related links using some tools. After this step, which we performed in a semi-automated way, we saved it on accessing the contents of the pages and analyzing them. The point of obtaining real intelligence will now depend on the correct correlation and storage of this data and the analysis of it.
At this point, we can use Maltego to visualize the data. Then, you can interact with the Kibana interface by holding the data on Elasticsearch and typing complex queries to strengthen the context.
As we mentioned at the beginning of our article, the main complicated and troublesome part is setting up the environment to be analyzed after the data is collected using OSINT techniques.
In this article, we discussed the technical difficulties and measures taken to address large-scale web crawls specific to the Tor network. Analyzing big data posed significant challenges. It will often be more effective to get a dark web intelligence service instead of designing these systems.
Conclusion
Open-source intelligence (OSINT) provides invaluable support for information security decision-making, offering insights into malicious activities that could potentially impact businesses. While OSINT on the surface web is more commonly utilized, using the Dark Web presents unique challenges that require advanced tools and methodologies. This article was crafted to provide a systematic perspective on how data collection and intelligence creation on the Dark Web can be approached effectively and securely.
As highlighted throughout the article, leveraging OSINT tools on the Dark Web requires careful planning and execution. From identifying onion links to processing the data collected, researchers and analysts face complex and evolving challenges. These challenges underline the importance of combining traditional OSINT tools with advanced solutions like those offered by Brandefense. With Dark Web Monitoring, Threat Intelligence, and Threat Detection, Brandefense empowers businesses to navigate the hidden layers of the internet safely and effectively.
This article aimed not only to showcase tools but also to raise awareness about the intricacies of Dark Web intelligence activities. The dynamic and decentralized nature of the Dark Web demands continuous adaptation and focus. With the solutions shared here, organizations can proactively detect threats, monitor malicious activities, and respond to risks in real time.
As threat actors evolve and new challenges emerge, staying ahead requires more than just tools—it requires actionable intelligence and reliable systems. Brandefense bridges this gap by integrating OSINT techniques with cutting-edge technologies, providing businesses with the insights they need to protect their digital assets.
For those looking to deepen their understanding of Dark Web monitoring or enhance their security posture, Brandefense stands as a trusted partner in the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats. Explore our solutions today and secure your future.