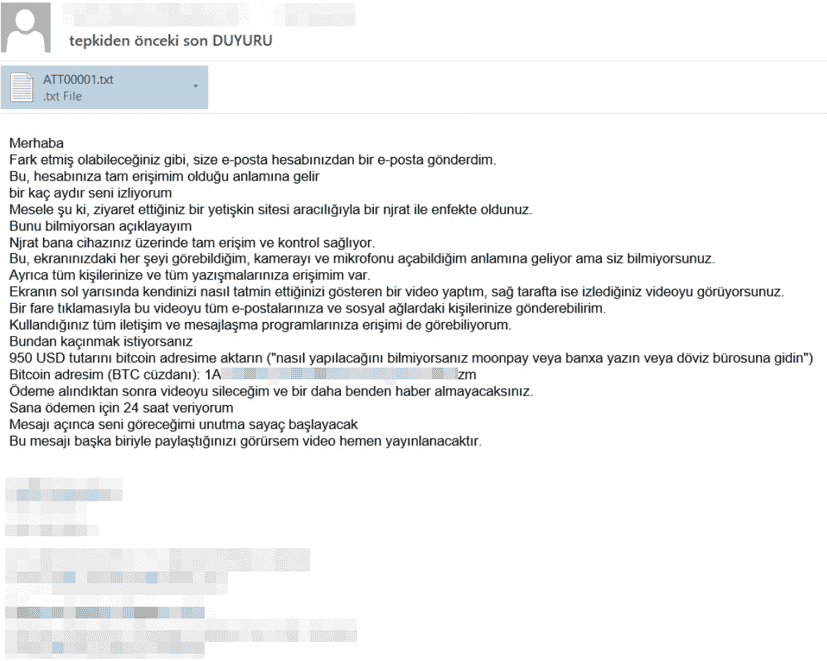
The attacker states that by infecting the target’s computer with malicious RAT software, for the target to pay the ransom amount, it takes over all the information about it, the accounts stored on the computer, and the computer. The attacker leaves a message in the target’s e-mail inbox by preparing an e-mail text explaining this situation. This e-mail appears to be sending an e-mail message to the user targeted by the attacker. But the actual situation is very different from what the attacker states in the statement.
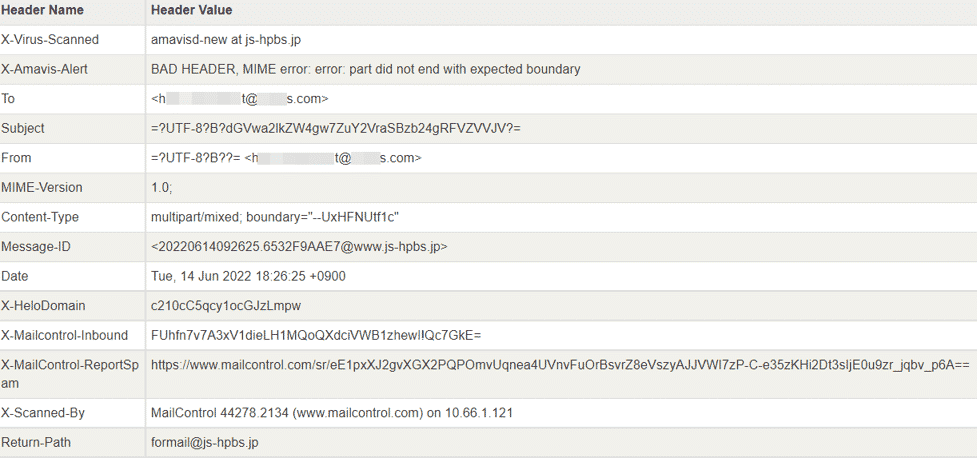
When we examine the e-mail header information, we see that the sender and receiver of the e-mail are the same accounts, but the e-mail server used during the e-mail transmission belongs to the domain js-hpbs.jp. The domain in question is registered under JustSystems Corporation, a software development company operating in Japan.
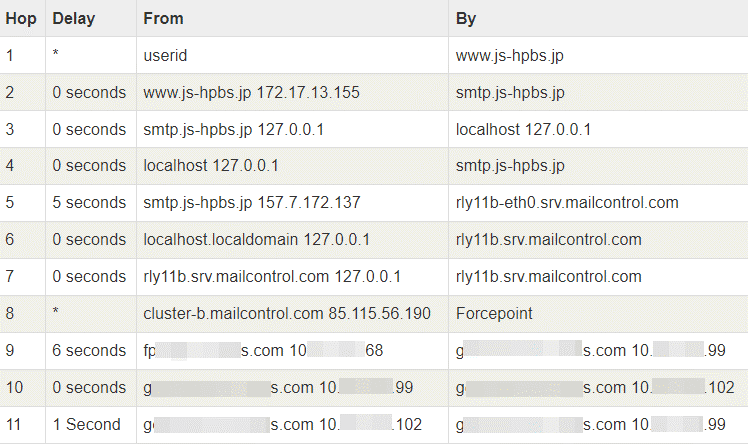
The e-mail transmission path shows the points through which the e-mail sent to the destination passes to the destination. In the detected campaign, it is seen that the output source of the e-mail is the SMTP server of the js-hpbs.jp domain. However, this does not match the header and forwarding path information that the attacker should have had when he left the threatening e-mail in the inbox of the targeted person.
The e-mails used in this campaign are not transmitted using a computer compromised with RAT software. Still, they are delivered in bulk to large audiences using an SMTP Relay Service. Therefore, the action taken by the attacker in this scenario is sending the e-mail on behalf of someone else by abusing SMTP Relay Service.
In summary, the campaign is based on making the target believe by intimidating that a fake security breach has been committed through malicious software and by having them transfer the ransom amount specified in the message to their Bitcoin account to prevent the spread of the allegedly compromised information.
What’s SMTP Relay Service?
Companies use the SMTP Relay Service to send large-scale marketing emails without managing an external email server of the SMTP Relay service. Thus, email servers do not fall into a blocklist.
Also, SMTP Relay Service is a type of phishing email spoofing that uses the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) to illegally send emails on behalf of another person or organization. This is done by gaining access to an SMTP server and using it to send emails that appear to come from a different sender.
Abusing of SMTP Relay Service
While this type of phishing attack is generally used to target senior executives or others who may have access to sensitive information, it has been observed that in cases encountered in Turkey, all personal information and images are seized from users’ computers via malicious RAT software and a ransom is demanded to prevent them from being published.
The attacker usually composes an email that appears to come from a trusted source, such as the company CEO or president. In some cases, an e-mail containing a ransom demand is left in the Inbox, claiming that the attacker has access to the attacker’s e-mail thanks to the RAT software. This looks like the user is sending an email to himself. The email usually contains some form of urgency, such as a request for urgent action or a warning about a security breach.
Prevent to SMTP Relay Spoofing
The common point of users exposed to SMTP Relay Spoofing attacks is using domains that do not have a DMARC policy configured with the “Reject” directive.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance), is an email authentication protocol that allows domain owners to specify what should happen if an email is spoofing their domain.
In addition, to protect yourself from SMTP Relay attacks, it’s important to be aware of phishing emails and to never respond to them. If you’re unsure about the legitimacy of an email, you can always contact the sender directly to confirm its authenticity. You should also make sure that your anti-virus software is up-to-date and that you have a firewall in place to help block suspicious emails.






