What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of cybersecurity attack during which threat actors send malicious emails designed to trick people into falling for a scam. By using illegal ways, phishing is stealing critical data (passwords, credit cards, personal information) of the targeted people. It is a type of attack used to steal confidential documents of institutions or organizations. Phishing is also known as the art of deception.
Attackers often impersonate a trusted source, which carries out attacks by creating a sense of trust in the targeted person. It can be carried out via social media or the phone, but the term “phishing” is mainly used to describe attacks via email. Phishing emails can reach millions of users directly and are hidden among the many bona fide emails that busy users receive. Additionally, with malicious software such as ransomware, attacks can infiltrate systems and take any action they want.
State-sponsored groups are trying to spy or steal data from the system with the help of malicious email attachments. They aim to carry out activities and benefit from a phishing attack as a first step. In addition, attacks can also occur from phishing sites designed to steal credit card data.
This article will discuss various techniques for catching phishing pages.
What Are Phishing Pages?
Phishing pages are a type of cyber threat that aim to trick users into exposing sensitive information, downloading malware, or transacting money by posing as a trusted website. These fraudulent websites are designed to seem legitimate and often use additional tactics like social engineering to gain victims’ trust.
Catching pishing pages can be challenging, as they often look exactly like the legitimate website they are mimicking. However, organizations can use some methods to detect them. This includes being cautious of unexpected emails or messages that ask for personal information and using phishing monitoring services that scan the web for phishing pages and alert users. In addition, Digital Risk Protection Services and Threat Intelligence Services are also practical tools for detecting and preventing phishing threats since they use advanced technologies and methods to identify and mitigate potential phishing threats. By staying on alert and using these tools and techniques, users can protect themselves against the dangers of phishing pages and keep their sensitive information safe.
Types of Phishing
Phishing tactics constantly evolve since threat actors find new ways to convince users to give away their personal and sensitive information. These are some of the current advanced phishing tactics:
Whaling
When attackers attack senior executives, such as members of an organization’s board of directors (“largest is called “fish”), it is called whaling (whaling). Attacks are usually personal messages of a senior executive, confidential documents, and high-level access to a corporate system. Theft of information falls under the type of whaling phishing. Whaling is one of the most severe and dangerous attacks because threat actors can access a large amount of company information with the knowledge of senior executives, a manager’s private. By distorting the identity in his life, the institution’s brand value is lowered in public opinion through the press. Various can be made to high-level managers.
Spear Phishing
Individuals are targeted instead of a large group of people, and information about the victims is provided before the attack. Specific attack scenarios are produced for the target person. Spear Phishing usually addresses an organization. It is the first step used to pass. Attackers analyze employees in the target organization. The weakest performs the phishing process on the ring it sees.
Pharming
Pharming redirects users to a fake website that appears to be trustworthy. However, it does not require victims to directly enter a harmful link to enter the fake site. Instead, attackers can infect users’ computers or websites; Even if site x is entered, they can redirect the user to a phony to y site.
Deceptive Phishing
In this attack, the attacker aims to steal victims’ credit card data or personal information. An example of Deceptive Phishing is a fake email asking the bank to verify your account information and a fake impersonation of the bank on the email website.
SMS Phishing (Smishing)
Smishing is a phishing method that uses text messages which seem to be coming from a well-known source, such as a shopping site or a governmental institution, and asks the recipient to click on a malicious link or provide sensitive information.
Voice Phishing (Vishing)
Voice phishing is a type of phishing method that uses voice calls to trick victims rather than emails or messages. Attackers may use spoofed phone numbers to be more realistic and seem to call from a trusted source, such as a federal agency or a bank. Also, they can use social engineering methods while talking to convince victims to share their passwords, account numbers, or other sensitive information.
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Business email compromise is a phishing method where attackers target businesses by gaining access to their email accounts. The attack aims to trick employees, partners, or customers into transferring money or sharing sensitive information. They usually start with an email that appears to be from a legitimate source and can be highly effective, causing significant financial and reputational damage.
Daily Recorded TLDs
The phishing keyword list is scanned with the Pedia tool so as to spend more days. In addition, this client-specific or general keyword list can be run. The previously prepared phishing keyword list should be scanned daily—TLDs with the help of a tool. Many resources share a list of paid and free TLDs. At this point, a customer-specific or general keyword list can be prepared and checked in daily lists.
Some of these TLD resources are:
- https://whoisds.com/newly-registered-domains
- https://zonefiles.io/
- https://dnpedia.com/tlds/daily.php
- https://www.whoisdownload.com/newly-registered-domains
Example keyword list:
- adobe‘
- ‘amazon‘
- ‘amaz0n’,
- ‘apple‘
- ‘bianca‘
- ‘binance‘
- ‘bing‘,‘
- ‘discord‘
- ‘microsoft‘
- ‘netflix‘
By writing a python script, we did a keyword search on the data drawn from the sources and reached potential phishing domains.

Similar Domain Detection
Domains with similar domain names can be detected and navigated. Various applications can be used to do this.
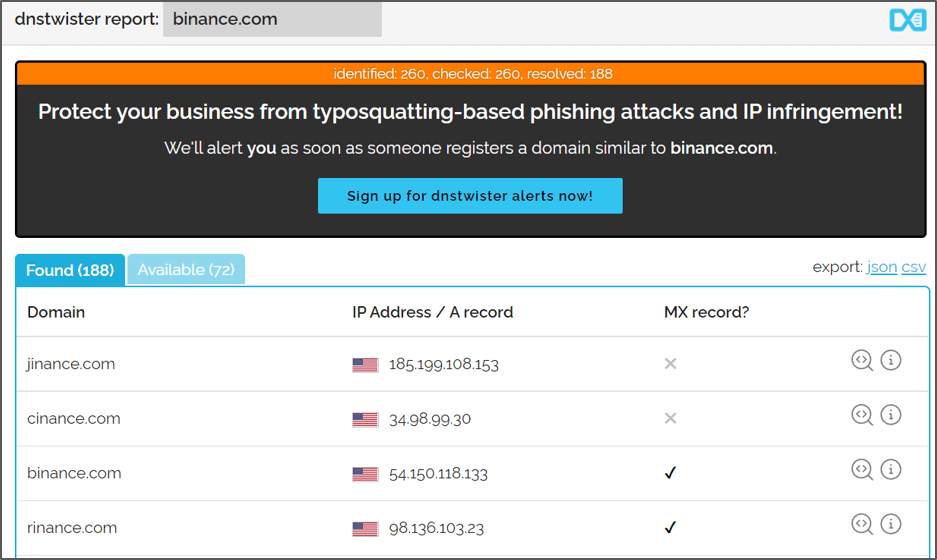
dnstwister.report
DNS Twister Provides an anti-phishing domain name search engine and DNS monitoring service. It can be used to find similar domain names.

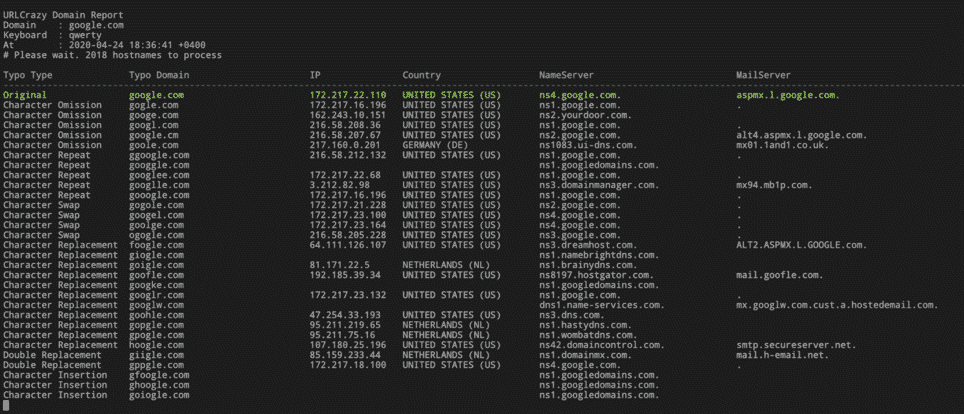
UrlCrazy
URLCrazy is one of the osint tools used to detect phishing activities.
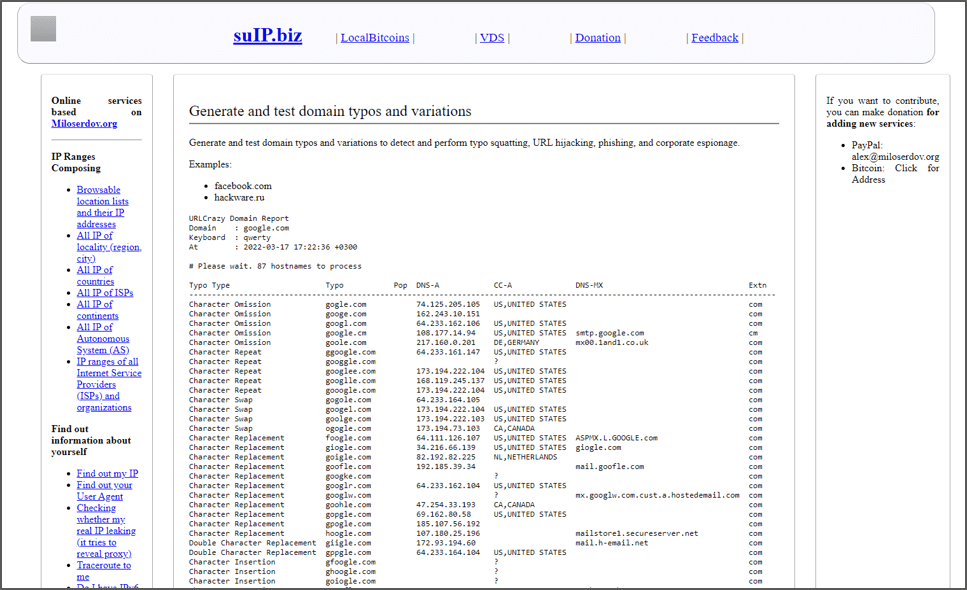
UrlCrazy WebApp
You can find the web version of URLCrazy at “https://suip.biz/?act=urlcrazy“.
A Case Study on the Phishing Pages
Detection and prevention of phishing pages is an issue that becomes more complex day by day. As threat actors develop their current methods, it is important to detect and take down phishing pages targeting your digital assets. More than one method can be used to detect phishing pages. In this case study, we will talk about the use of favicon and MMH3 hash, which is a detection method.
We can use the favicon hash value to find phishing pages. A favicon, also known as a shortcut icon, is a file containing one or more small icons associated with a particular website or web page.
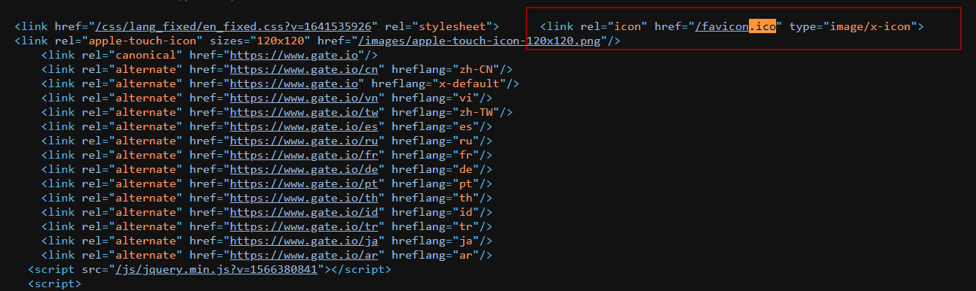
Favicon links can be found in the web page source code with the .ico extension (can be viewed by pressing Ctrl+U, F12, or right-clicking and “view page source”).
In the case of phishing sites, the icon of the actual site is often copied or directly linked from the original impersonated page to support the impression of legitimacy. At this point, it can be searched with Shodan or other IoT search engines by taking the favicon hash value.
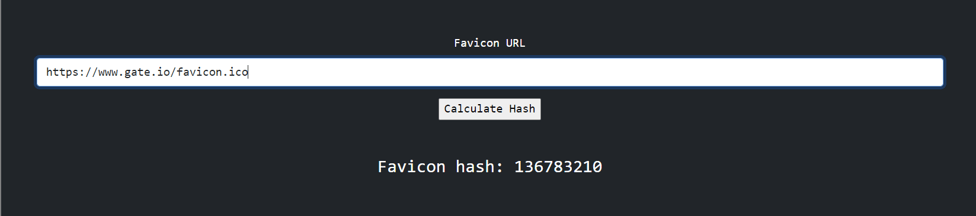
We can get a hash value in MMH3 format of the favicon links we find on ‘faviconhash.com.’ MMH3 is a Python wrapper for MurmurHash (MurmurHash3), a set of fast and robust non-cryptographic hash functions. Also, the same operation can be performed using the following repo.
https://gist.github.com/yehgdotnet/b9dfc618108d2f05845c4d8e28c5fc6a
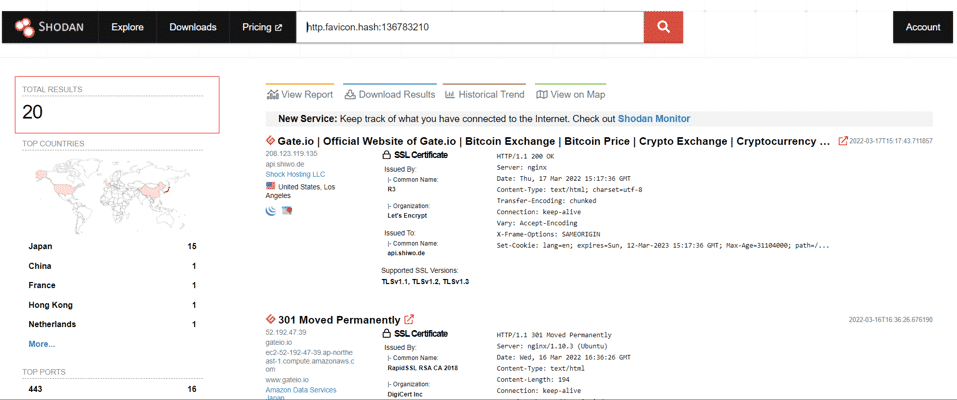
In the next step, other sites using the same favicon will be detected by making queries with the favicon hash value in Shodan and other IoT search engines.
The image hash can also be used to detect phishing pages. The hash value we generate using the SHA256 algorithm is a unique numeric fingerprint that is the sum of the components of a file. Different mathematical methods are used to create a unique fingerprint for a file. SHA256 algorithm generates an almost-unique, fixed-size 256-bit (32-byte) hash. Hash is so-called a one-way function. This makes it suitable for checking the integrity of your data.
We get the hash value by downloading any image on the actual page.
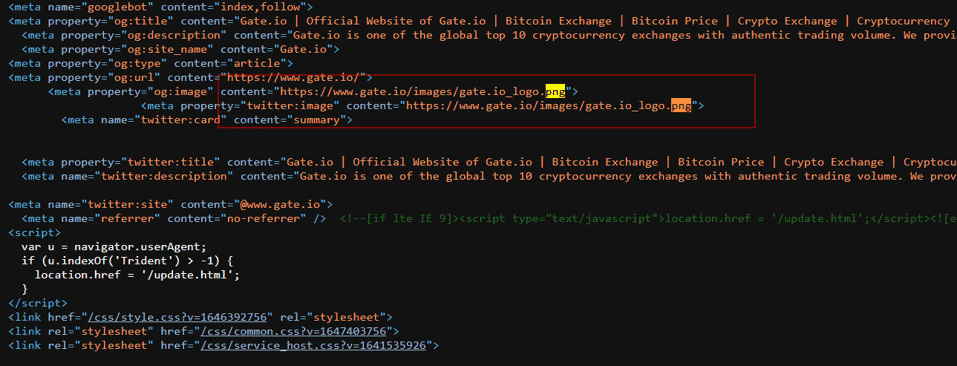
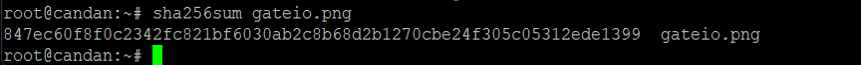
When we query the hash value on ‘urlscan.io’, we see that there are some phishing pages that use the same image.
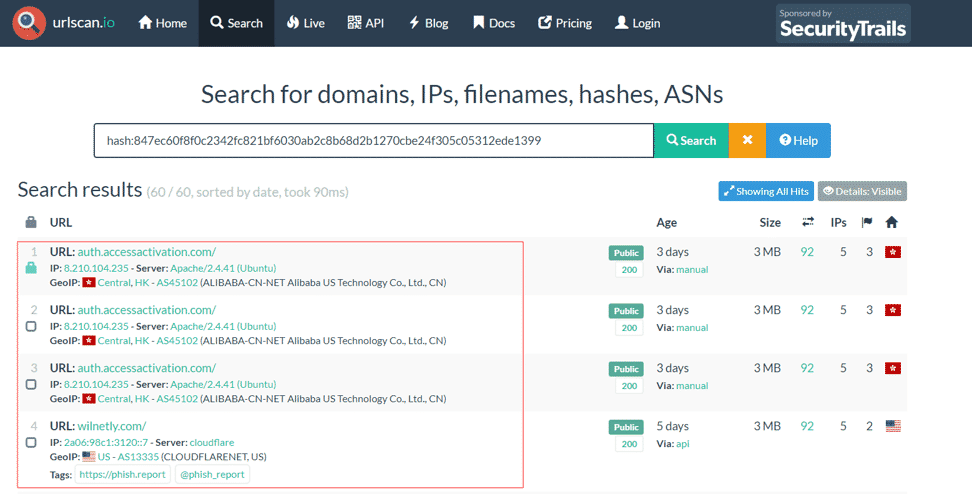
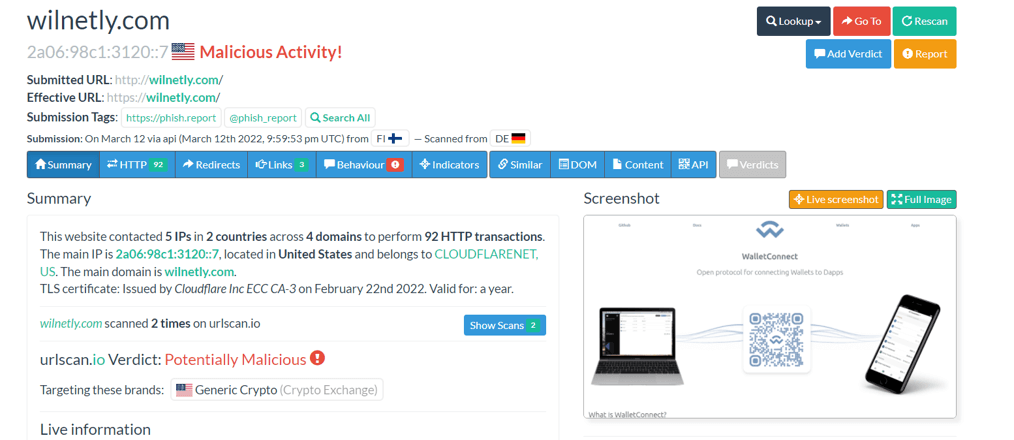
Ways to Avoid Phishing Attacks
- The systems used should be kept up to date.
- The links to be redirected should be checked.
- The address of the person or organization sending the mail must be verified.
- Whois records should be checked for suspicious websites.
- Do not interact with links, attachments, or redirects in involuntary pop-up windows.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) should be activated on the platforms used.
- Corporate e-mail addresses and membership transactions in different and irrelevant applications should be avoided.
- Files in e-mail attachments should be checked on platforms such as Virustotal.
- Social engineering awareness should be instilled in the employees of the institution.
- Access to unapproved web applications should be blocked.
- SSL encryption certificate (HTTPS) check should be done on the logged-in and logged-in web pages. If you are logged into pages without SSL encryption, the current password should be updated with a strong one.
- Entry and exit activities in the accounts should be checked regularly.
- Licensed and official anti-virus applications should be preferred for client computers or systems.
- Personal information should not be shared with any unreliable institution. For example, people who state that they provide access from the bank should ask for the credit card information of users.
Authors:
Ahmet Candan
Görkem Güler
Doğuhan Okan Gül