Ransomware: A Rising Danger to Business Operations and Data
Ransomware is a malicious attempt to take control of your data and demand payment for its return. Attackers usually use phishing emails, links in email attachments, social engineering tactics, or vulnerabilities within unpatched software systems as entry points into an organization’s network. Once installed on a target device, ransomware can quickly spread to other connected devices, causing significant disruption. This can lead to lost revenue from system outages, damage to customer trust, and potentially devastating losses due to loss of access to critical business information and data files.
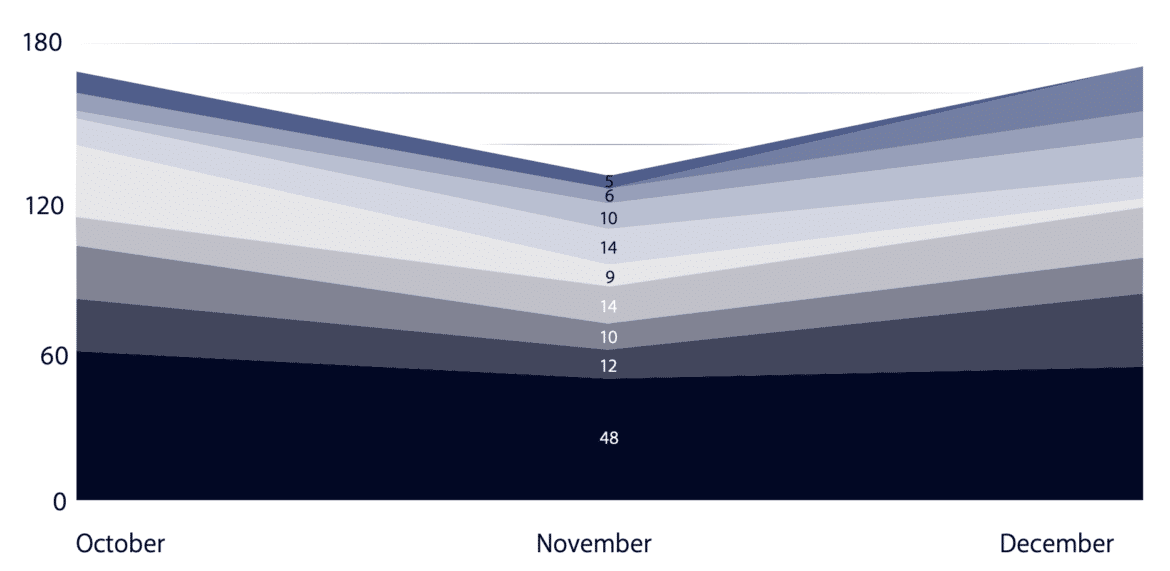
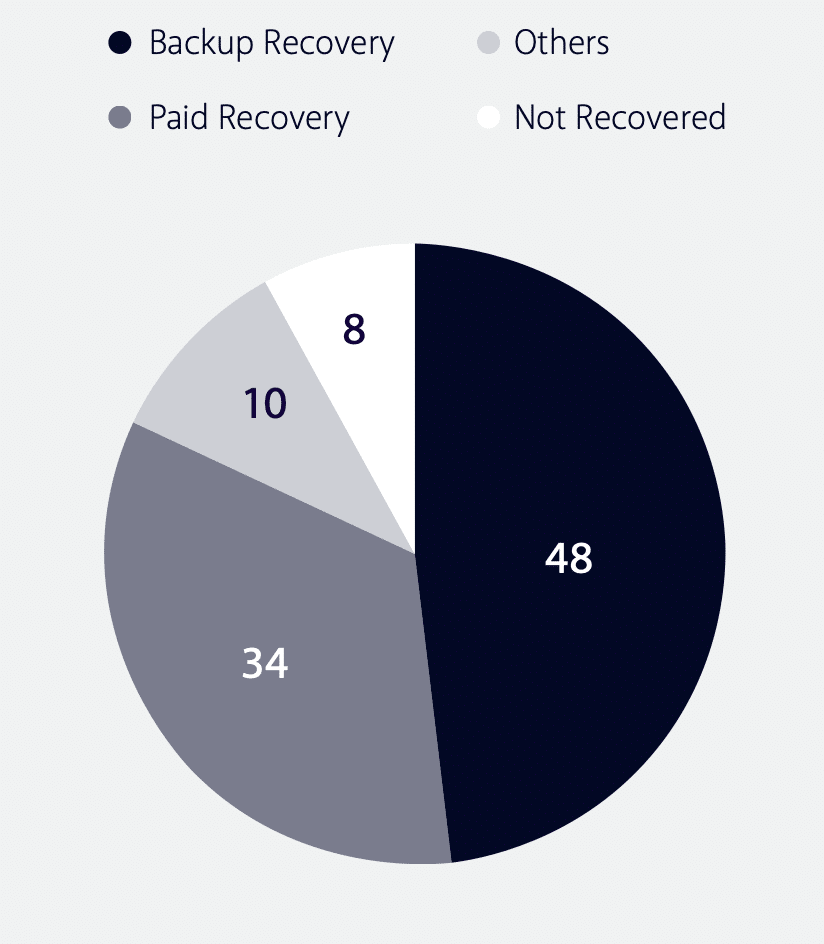
Ransomware Attacks Increase: The Dilemma of Paying Ransom to Restore Encrypted Data
Ransomware attacks have become increasingly common in recent years and can be devastating for individuals and organizations. In many cases, the attackers will demand a large sum of money in exchange for the decryption key needed to restore access to the encrypted files. Victims who do not have backups of their data may feel forced to pay a ransom to prevent the permanent loss of their essential files. However, paying the ransom does not always guarantee that the attacker will provide the decryption key, so it is generally not recommended.
Exploring the Methods: How Ransomware Groups Target Organizations
Understanding the Tactics: Phishing Emails, Vulnerabilities, and Insider Threats
Ransomware groups typically target organizations because they are more likely to have valuable data and be willing to pay a ransom to restore access to it. These groups often use a variety of tactics to target organizations, such as sending phishing emails with malicious attachments, exploiting vulnerabilities in software or systems, or compromising a network through an insider threat. Once a ransomware group has gained access to an organization’s network, they typically use automated tools to spread the malware throughout the network, encrypting as many files as possible. The attackers will then usually demand a ransom payment for the decryption key, which is needed to restore access to the encrypted files.
Standard methods that hackers use to spread ransomware
Ransomware can exploit several attack vectors to take over computers or servers. The most common method for hackers to spread ransomware is through phishing emails. Hackers use carefully crafted phishing emails to trick a victim into opening an attachment or clicking on a link that contains a malicious file. The principle behind the strategy is that it only takes one person to click on the link to enable cyber attackers to infiltrate an entire organization.
They use social engineering techniques to create emails that make sense from a corporate perspective and have the same tone of voice and format as legitimate messages. They lower victims’ skepticism and increase their chances of a successful phishing attempt.
Discuss other methods, such as Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and drive-by downloads.
Another increasingly popular mechanism in which attackers infect victims is through Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). Engineers designed Remote Desktop Protocol to enable IT administrators to securely access users’ machines remotely for configuring, troubleshooting, updating, and usage. RDP typically runs over port 3389. While opening doors to a device for legitimate use has many benefits, it also presents an opportunity for a bad actor to exploit it for illegitimate use. In 2017, Researchers determined that over 10 million machines advertise themselves to the public internet as having port 3389 open.
Another entry path that attackers use to deliver ransomware is through what is known as drive-by downloads. When they visit a compromised website, these malicious downloads happen without users’ knowledge. Attackers often initiate drive-by downloads by taking advantage of known vulnerabilities in the software of legitimate websites.
How to prevent it?
It is essential to take steps to protect against ransomware attacks. Ransomware attacks include
- keeping your computer’s software up to date,
- using a reliable antivirus program and
- avoiding opening suspicious email attachments or links.
It is also a good idea to regularly back up your important files so that you have a copy in case your computer is infected with ransomware. Suppose you do fall victim to a ransomware attack. In that case, you should immediately disconnect your computer from the internet and seek help from a professional to help you restore your files and protect against further attacks.
This blog post comes from the “2022 Q4 Ransomware Trends” by the Brandefense CTI Analyst Team. For more details about the analysis, download the report.






