Overview
The proliferation of technological infrastructures with digitalization meets the needs of institutions and leads to an increase in cyber security gaps and thus security threats. The possible risks are listed as follows and the analyses made in recent years.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is malware that prevents a user from accessing their computer and critical files, thereby demanding ransom. The threat actors’ desire to generate large amounts of revenue in a short time leads to an increase in ransomware threats since its distribution and use do not require technical skills.
In ransomware attacks, files within the scope of assets to be protected for the person/organization are encrypted, and the user is prevented from using these files. In addition, payment is made in virtual currency to recover sensitive data and prevent it from being shared publicly. If the victims don’t pay the ransom, sensitive data will be lost and shared publicly.
Trends of Ransomware
Double Extortion
When ransomware first appeared, it encrypted files with various encryption algorithms and deleted them from the target system to demand a ransom payment. However, threat actors are developing new methods for institutions that realize the ransomware threats and make the necessary backups. One of them is called Double Extortion.
Threat actors not only encrypt files but also leak data from the target system, threatening to publish or sell it publicly.
Triple Extortion
The latest trend that ransomware groups are starting to use is the Triple Extortion method. The main goal is to pressure targets to pay the ransom.
In Triple Extortion, in addition to the ransomware encrypting files and leaking them from the target system (Double Extortion), DDoS attacks are carried out on the network infrastructure of the target organization. This trend of attacks will also indirectly affect victims’ assets such as users, clients, and service providers.
Popular Ransomware Attacks and Actors
- ACER: $50 million ransom was demanded.
- Colonial Pipeline: Ransom of $4.4 million was demanded.
- KASEYA: Ransom of $70 million was demanded.
- Lockbit2.0
- Conti
- Darkside
- REvil
- Ragnar
Ransomware Statistics
- In 2021, ransomware attacks cost $20 Billion. This number is expected to rise to $265 billion by 2031.
- In 2021, 37% of organizations worldwide were affected by ransomware.
- It cost an average of $1.85M in 2021 to recover data from ransomware.
- While 32% of ransomware victims agree to pay the ransom, they only get 65% of their data back.
- 57% of victims successfully recover their data using backup.

How do you protect yourself from Ransomware?
- Keep regular backups of your assets that need to be protected in environments without internet access.
- Train your staff against common phishing attacks.
- Use IDS/IPS systems that can block existing hacking attempts.
- Upgrade used apps to the latest version.
What are Insider Threats?
It is a common type of attack that can occur intentionally or unintentionally within the framework of corporate personnel and negatively affects corporate reputation. It can be done for financial gain, or sensitive data can be leaked if the relevant security procedures are not followed.

Insider threats can harm the organization through the situations listed below:
- Espionage
- Terrorism
- Disclosure of information
- Sabotage
- Intentional or unintentional loss or degradation of department resources or capabilities
Insider Threat Statistics
- In 2020, 60% of data breaches were caused by Insider Threats.
- 67% of unintentional Insider Threat incidents still occur with phishing attacks.
- 94% of distributed malware originates from email.
- Attacks from Insider Threats cost organizations $871,000 per incident.
How do you protect from Insider Threats?
- Employees should train on security processes.
- Access to sensitive data should be restricted.
- Double factor protection should be used in the systems used.
- Check the history of employees, especially those who need access to sensitive data.
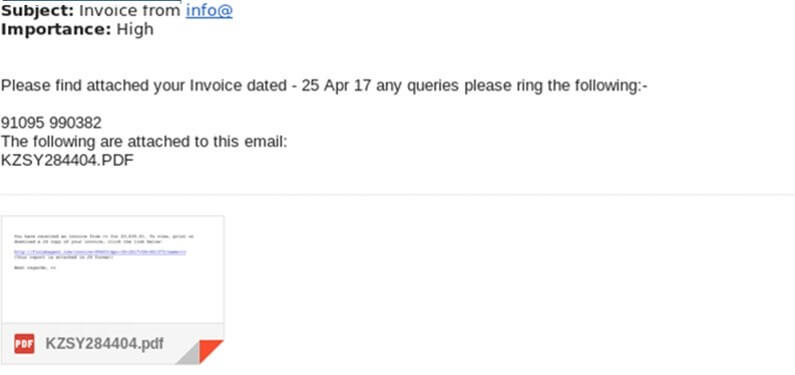
What is Phishing Attack?
Phishing is a social engineering attack that is often used to obtain user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers. Attackers try to persuade users to click on a link that could download malware or redirect them to a dangerous website.
In the phishing methods, which constitute the first stage of almost every cyber attack, the targets are tried to be deceived by the attackers with fear, anxiety, or offers that are too tempting to be true. In addition to the abuse of such feelings, phishing attacks can organize through copies of actual documents.
Phishing Attack Statistics
- Approximately 15 Billion emails are sent daily, and 45% of these emails are spam emails.
- 30% of sent phishing messages are opened.
- 66% of malware is installed with malicious email attachments.
- 97% of people fail to identify a phishing scam.
How do you protect from Phishing Attacks?
- Emails and links from unknown sources should not be respected.
- Suspicious messages should be cleared from the platforms used.
- Network intrusion detection systems and email transmission paths can be used to detect phishing emails containing malicious email attachments. The solutions that can use for this can be signature or behavior-based. In addition, DKIM+SPF checking or filtering based on email header analyzes can give details about possible attack attempts.
- Using anti-virus solutions on the email server or user computer can help detect malicious files and attachments. In addition, it can be helpful to monitor sub-processes created by software associated with Microsoft Office or other documents.
What are Cloud Attacks?
The popularity of the concept of cloud computing is being used more and more widely thanks to big players such as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft that provide cloud computing platforms. This process, which generally starts with backup, is included in the companies’ storage, sharing, and information processing processes along with the needs.
Also, as cybersecurity experts know, anything that becomes popular in the digital world will inevitably become the target of malicious cyber actors.
Types of Cloud Attacks
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
- Malware Injection Attack
- Side-Channel Attack
- Network-based co-residence check
- Brute forcing
- Authentication and MiTM Attack
- Hypercall Attacks
- Hyperjacking
- Exploiting Live Migration
How do you protect from Cloud Attacks?
- Cloud users must ensure that the data stored in the cloud is encrypted and keep the key securely, as they lose a great deal of control over the hosting process after moving their data to remote servers.
- Detect side-channel attack only during the deployment phase. It can be done by collecting records for start and stop machines and importing them into a SIEM solution.
- A large number of new machines appearing and shutting down in a defined time may indicate that an attacker is performing unusual activities.
- Instead of simple username and password verification control, strong password creation policies should be established, and multi-factor authentication should be implemented.
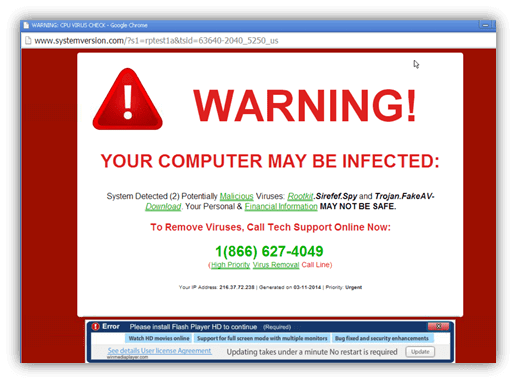
What are Malvertising Attacks?
Malware has long been one of the attack vectors used by threat actors. Attackers now use malicious ads to appear more legitimate to their targets, thereby infecting target systems with malware.
With this technique, attackers redirect users to malicious websites or inject code into advertisements that will directly install malware on the device. The malicious ads used can be difficult to spot as they are paid through legitimate ad providers.
How do you protect from Malvertising Attacks?
- Ad blockers and script execution blocking browser plug-ins can be used to prevent malicious content distributed through advertisements and the use of JavaScript during exploitation.
- Firewalls can perform reliability-oriented queries on the URLs that the user wants to visit, including checks such as the registration date, the number of visitors, and the history of malicious activity.
- IDS systems are used on network discovery, browser identification, etc. It can detect malicious scripts such as exploit codes and common hiding techniques of these codes.
Conclusion
Organizations that adopt digitalization with rapidly developing technologies can significantly reduce the threats against them without creating an excellent cyber security infrastructure and implementing audit policies.
We aimed to create reference points so that you can find the steps that can be taken to reduce the attack vectors with an overview of the cyber threats that may be against every institution/organization regardless of the sector.
References
- https://cloud.netapp.com/blog/blg-cloud-malware-5-types-of-attacks-and-3-security-measures
- https://www.malwarebytes.com/malvertising
- https://attack.mitre.org/tactics/enterprise/
- https://www.cisa.gov/defining-insider-threats
- https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/threats/ransomware
- https://www.cloudwards.net/ransomware-statistics/
Authors:
Duysal Kantarcı
Gökhan Fırat
Şafak Çebin






