In the MailChimp breach, an unknown threat actor hijacked internal tools used by the company’s customer support staff for account management. This social engineering attack that targets MailChimp’s employees resulted in the hijacking of employee credentials.
After the MailChimp attack, users of the Trezor crypto wallet that hardware that allows users to store their cryptocurrencies offline reported receiving suspicious e-mails about a security incident related to the company. These e-mails received by users are part of a carried out phishing attack through captured data in the MailChimp attack.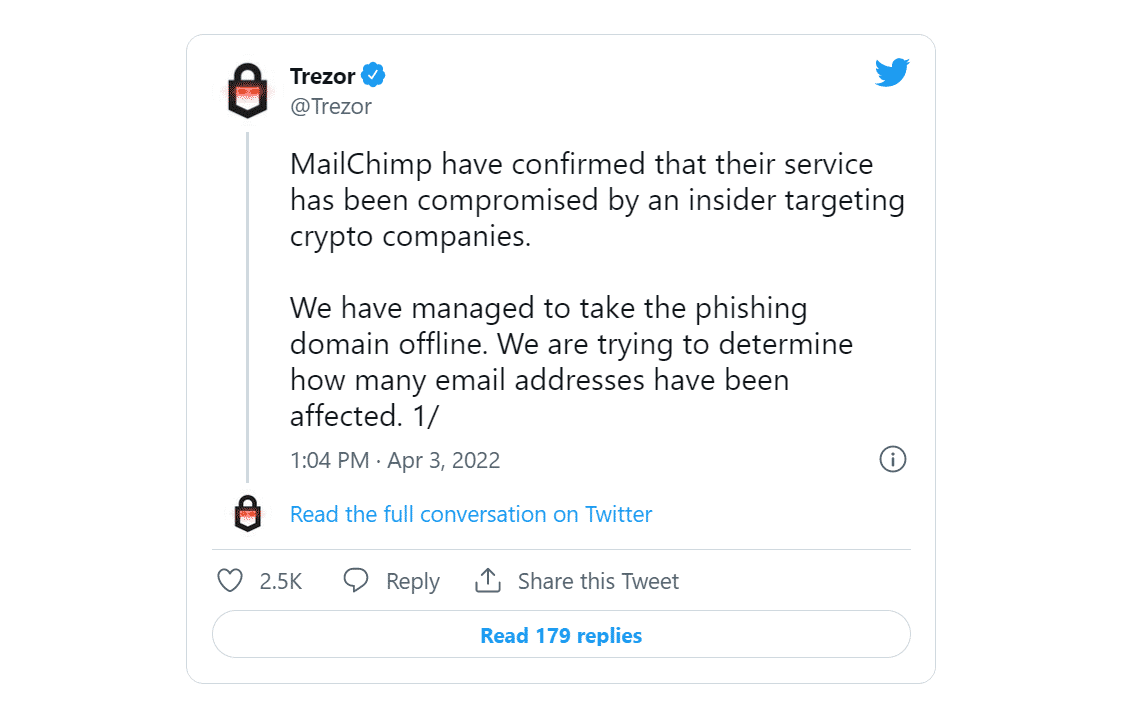
In this context, it is recommended to disregard e-mails and links that seem to come from Trezor, change the information used in MailChimp accounts using strong policies, be aware of leaked data, and enable 2FA/MFA features on used platforms. In addition important to raise awareness of institution/organization personnel against possible phishing or social engineering attacks.






