Critical Authentication Bypass Security Vulnerability Detected in Atlassian Jira
Jira and Jira Service Management products developed by Atlassian have been identified to be affected by an authentication bypass vulnerability that exists in Jira Seraph, the web application security framework. In Seraph, Jira, and Confluence, it is a security and authentication framework used to process all login and logout requests.
The vulnerability, tracked with code CVE-2022-0540, allows a remote threat actor to bypass authentication by sending a specially crafted HTTP request to vulnerable endpoints.
The vulnerability, rated as critical, affects Jira Core Server, Software Data Center, Software Server, Service Management Server, and Management Data Center solutions. The versions of the affected solutions are as follows:
- Jira Core Server, Software Server, and Software Data Center before 8.13.18, 8.14.x, 8.15.x, 8.16.x, 8.17.x, 8.18.x, 8.19.x, 8.20.x before 8.20.6 and 8.21.x versions are affected.
- Jira Service Management Server versions earlier than 4.13.18 and Management Data Center, 4.14.x, 4.15.x, 4.16.x, 4.17.x, 4.18.x, 4.19.x, 4.20.x and earlier than 4.20.6 Versions 4.21.x are affected.
It is known that security vulnerability does not affect versions of Jira and Jira Service Management Cloud. Atlassian releases security updates for affected versions. Users who use vulnerable versions are advised to immediately upgrade to the current releases to not be the target of attacks that can be carried out using this vulnerability.
Rocket Kitten APT Exploit VMware RCE Vulnerabilities in Backdoor Distribution Campaigns
It has been detected that the Iranian-connected Rocket Kitten threat actors have recently distributed “Core Impact” malware through an updated VMware RCE security vulnerability.
The vulnerability monitored by code CVE-2022-22954 and affecting VMware Workspace ONE Access and Identity Manager solutions cause RCE attacks that allow the threat actor to access with high privileges. Threat actors who use this vulnerability to access the target system then deploy the Core Impact Backdoor to memory using the PowerShell script called PowerTrash.
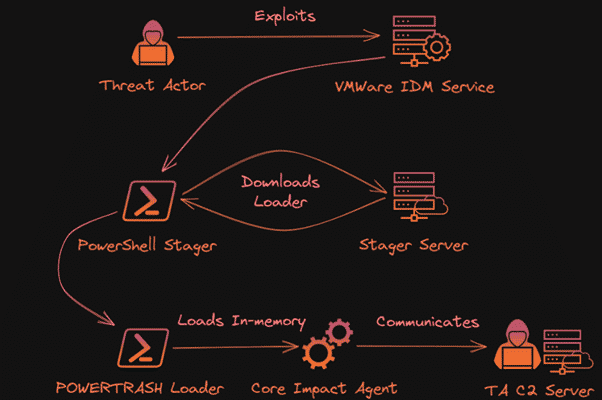
The widespread use of VMware Identity Manager solutions and unlimited remote access to threat actors from this attack can lead to destructive breaches among industries.
In this context, it is recommended that users using vulnerable VMware products immediately apply the published updates to protect against attacks that can be carried out using the said vulnerability. In addition, it is important to prevent the IoC findings related to the campaign in question from the security solutions used.
A Cryptographic Security Vulnerability Detected in Java: “Psychic Signatures”
A cryptographic security vulnerability has been detected by security researchers in Java that allows threat actors to potentially capture communications and messages that should be encrypted, such as SSL communications and authentication processes (JWT).
The security vulnerability, called “Psychic Signatures,” monitored as CVE-2022-21449, is due to the incorrect application of the signature verification algorithm (ECDSA). Effective use of vulnerability results in the void of the integrity of content guaranteed by signatures.
The vulnerability affects Java 15, 16, 17, and 18 versions. In this context, it is recommended to immediately upgrade the vulnerable Java versions to the latest version (17.03 or 18.0.1) not to be the target of attacks that can be carried out using the vulnerability.
Three Critical Vulnerabilities Detected Affecting Cisco Products
Network solutions provider Cisco has released updates to address high-severity security vulnerabilities that could allow threat actors to take control of affected systems and carry out denial-of-service attacks (DoS).
The details of these security vulnerabilities are as follows:
- The vulnerability, tracked by code CVE-2022-20783 and due to lack of authentication, affects Cisco TelePresence Collaboration Endpoint (CE) Software and Cisco RoomOS Software.
- The vulnerability tracked by code CVE-2022-20773 and found in Cisco Umbrella Virtual Appliance (VA) relates to a static SSH host switch that allows threat actors to perform potential Man-In-The-Middle (MitM) attacks.
- The vulnerability, tracked by code CVE-2022-20732, could allow threat actors to view and modify database content to elevate their privileges on the affected device.
Cisco has also fixed many medium-severity vulnerabilities affecting other products in its product line, including Webex Meeting, Unified Communications Products, Umbrella Secure Web Gateway, and IOS XR Software. In this context, it is recommended to immediately upgrade the vulnerable versions to the published updates in order not to be the target of attacks that can be carried out using vulnerabilities.
Enterprises GitHub Repos Are Targeted through Captured Auth0 Access Tokens
A cloud-based storage service, GitHub, has announced that threat actors manipulate 0Auth user access tokens to commit data breaches from enterprise GitHub repos. With the detection of transactions by threat actors on April 12, 2022, it has been observed that the data of many organizations, including NPM, were seized using 0Auth access tokens belonging to Heroku and Travis-CI applications.
OAuth access tokens are often used by different services and applications to authorize access to designated parts of user data and communicate with each other without sharing credentials. This is based on the SSO (Single Sign-on) architecture, allowing single login to authorize other applications.
Github authorities have issued a statement stating that 0Auth access tokens will not be obtained by a data breach on GitHub and that these tokens are not stored directly in a usable format. Also has been detected by GitHub security researchers that unauthorized access to the NPM’s development environment has been made through a compromised AWS API key. It is estimated that the threat actors obtained the API key using the 0Auth access tokens captured. Github took action following an increase in activities using 0Auth access tokens, preventing the use of such tokens.
According to Github’s statement, some Github repositories have been compromised, but no changes have been made to the packages, and no user data or credentials have been accessed. Github has launched a detailed investigation to identify all users and organizations affected by the breach. It is recommended that GitHub users who have the potential to be affected by this breach regularly review OAuth applications that they are authorized or have access to their organization and periodically follow the security logs of the relevant organization to identify potential anomaly activities.
New Zero Click Vulnerability Detected Affecting iOS Operating System
Citizen Lab digital security researchers have detected a new zero-click iMessage vulnerability, which is used to install Pegasus spyware on the iPhone devices of Catalan politicians, journalists, and activists. Pegasus is developed by the Israeli firm NSO and marketed to governments as licensed software for investigating terrorist activities. With Pegasus spyware, attacks were carried out on high-level authorities of many states such as the United Kingdom and Finland.
Between 2017 and 2020, it was observed that Pegasus targeted at least 65 people by exploiting the Kismet iMessage vulnerability and a vulnerability in Whatsapp. Many people are among the recently observed campaign targets, such as Catalan members of the European Parliament, heads of state, judges, lawyers, and journalists.
The zero-click vulnerability, called HOMAGE, affected some versions before iOS 13.2 and was fixed in iOS 13.2. In the statement made by Apple officials, it was stated that users using the current version of iOS are not affected by the HOMAGE exploit. Spyware installed on target systems without any user interaction (zero-click) comes with many features such as reading messages on devices, listening to calls, capturing user passwords, location tracking, and accessing the device’s microphone and camera.
The campaign in question has not yet been attributed to any state or threat actor, but the findings indicate that the campaign was carried out by threat actors affiliated with the Spanish government.
In this context, in order not to be the target of attacks that can be carried out using the said vulnerability and malicious software, it is recommended to keep the device/system or programs used in the latest version, download applications from official sources, and use a comprehensive anti-malware solution.






