RedAlert: The New Ransomware Targeting VMware ESXi Servers
A new Ransomware called RedAlert (N13V) has been detected targeting VMware ESXi servers installed on both Windows and Linux systems in attacks on corporate networks.
The Linux encryptor is designed to focus on VMware ESXi servers and has command line parameters that allow threat actors to shut down running virtual machines before encrypting the file. The malware, which has been observed to use the NTRUEncrypt algorithm for encryption operations, only targets files associated with VMware ESXi servers, such as log files (.log), swap files (.vswp), virtual disks (.vmdk), and memory files (.vmem).
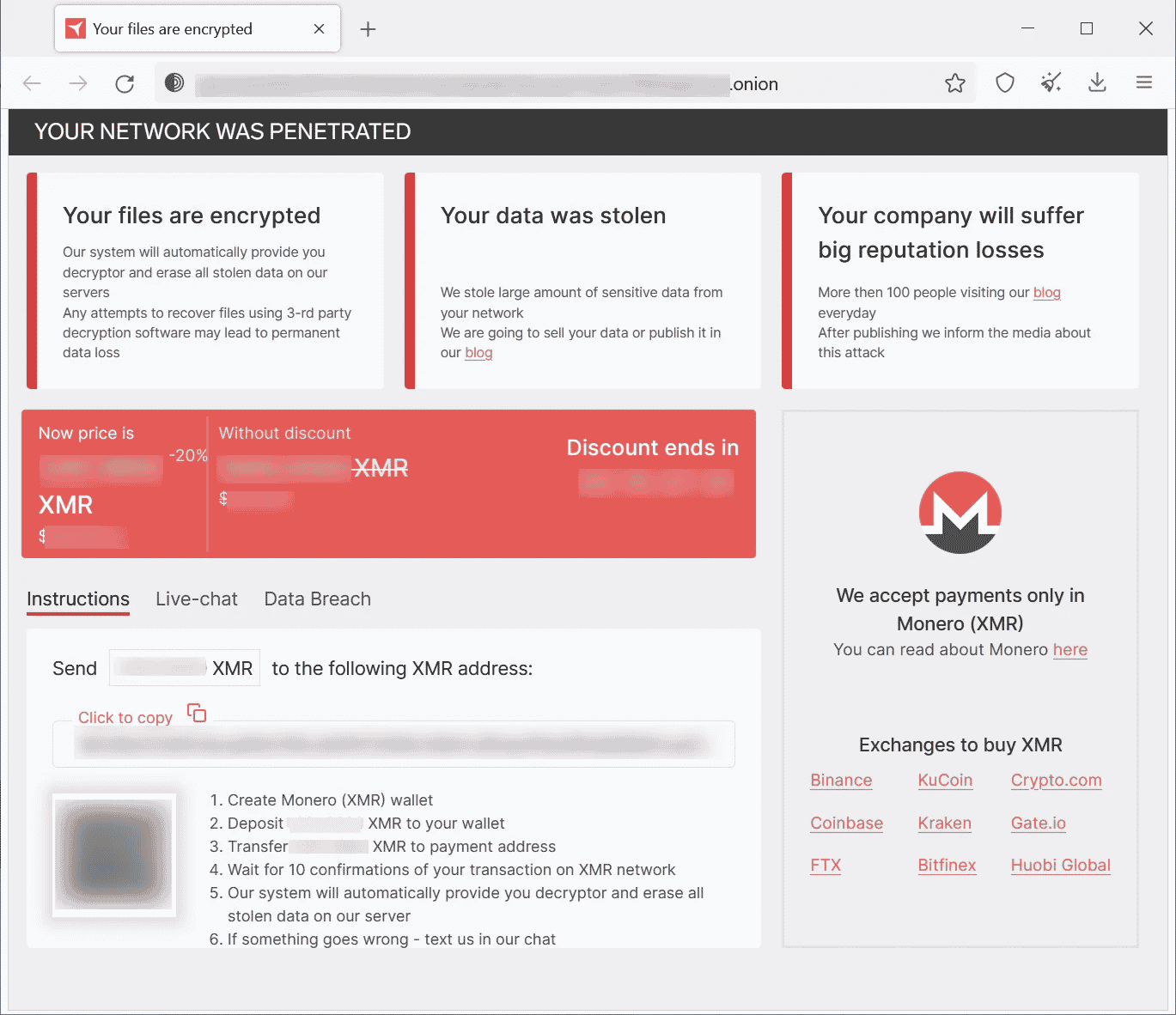
In the sample analyzed by security researchers, it was observed that the Ransomware software added the “.crypt658” extension to the filenames of encrypted files. A ransom note named HOW_TO_RESTORE, which is observed to be added to each folder by the ransomware, contains a description of the data compromised and a Tor link that directs victims to the ransom payment site. The payment page on the Tor network is similar to other Ransomware operation pages where a ransom demand is shown, and options are offered to negotiate with threat actors. RedAlert/N13V threat actors only accept Monero cryptocurrency for ransom payment.

In order not to be the target of similar ransomware attacks that may be carried out in this context, it is recommended to take the following actions;
- Beware of unreliable e-mail contents,
- Suspicious e-mail attachments and links should not be respected,
- Using reliable Anti-Malware solutions,
- Using licensed and up-to-date technologies,
- Used security solutions should block shared IOC findings regarding the malware campaign.
Marriott International Suffered from Security Breach Leading to 20GB of Data Hijacking
Hotel chain Marriott International has confirmed that it has suffered a new data breach that resulted in the hijacking of 20GB of internal data by threat actors. In this breach, threat actors compromised the BWI Airport Marriott Maryland (BWIA) network.
About a month ago, threat actors gaining unauthorized access to the BWI Airport Marriott network seized 20GB of data allegedly containing credit card, reservation, flight information, and internal confidential business documents belonging to Marriott customers. After the breach, threat actors informed many company employees about the breach. As a result, it is known that Marriott International officials refused the ransom payment demanded by the threat actors and launched a joint investigation with law enforcement officials for the unauthorized access, which was brought under control within about six hours. Images of some documents that are stated to have been seized by the threat actors in the breach are given below:
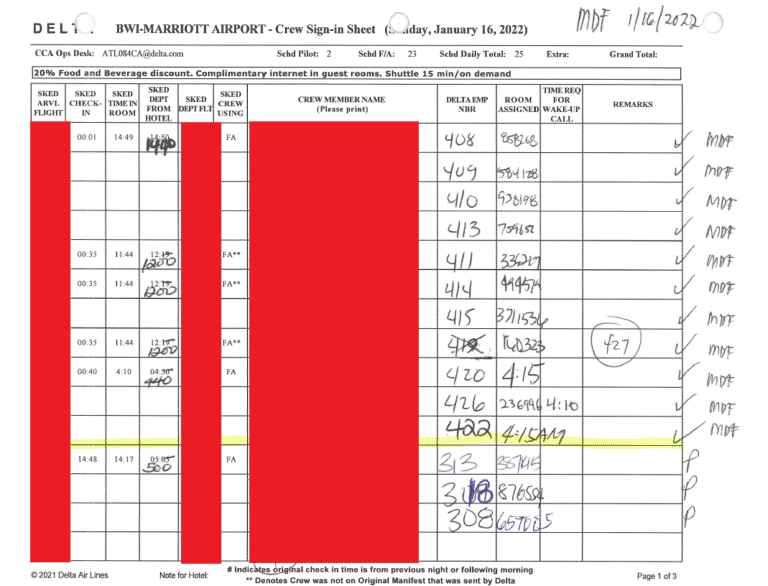
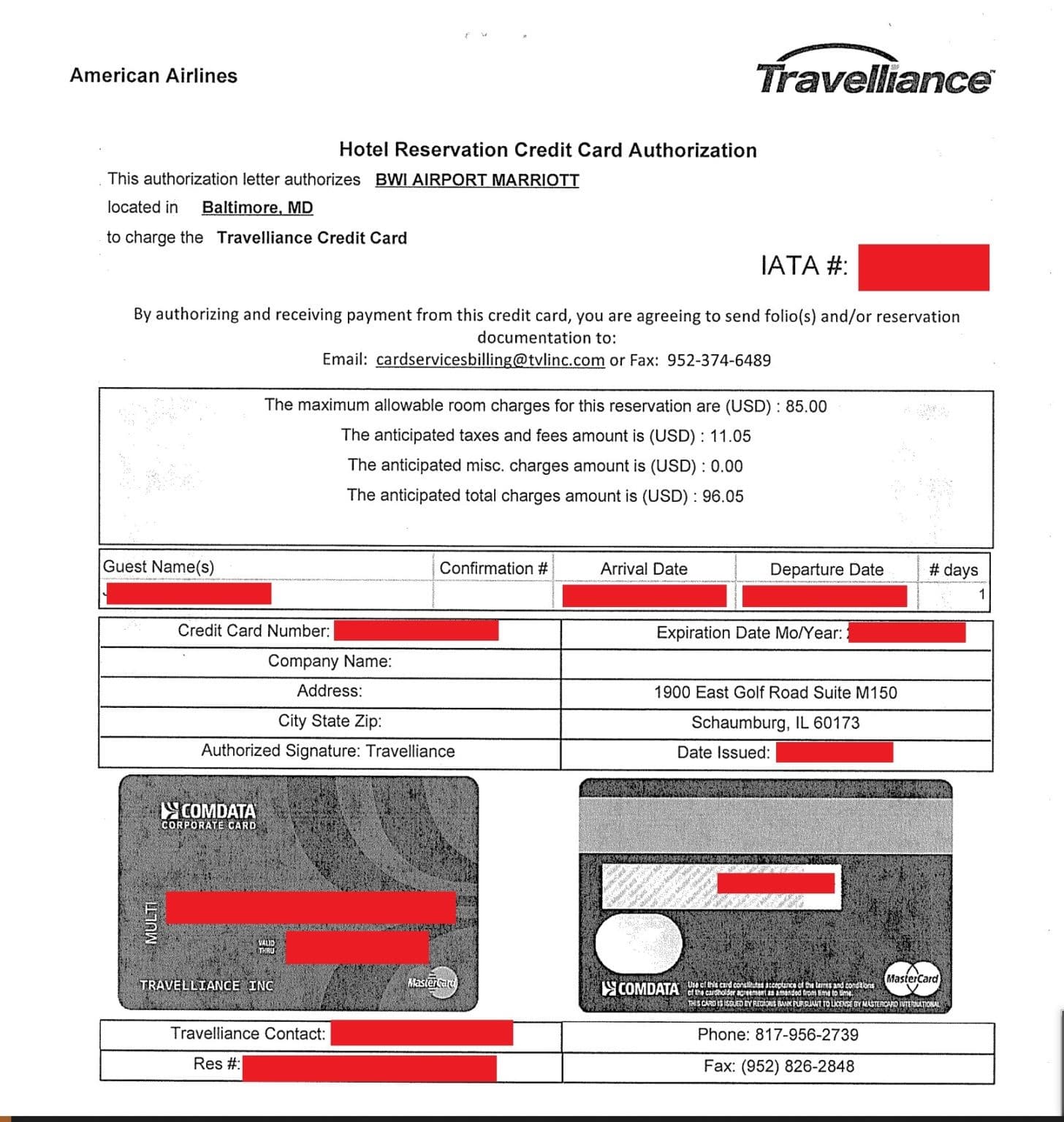
Although Marriott International, known to have been exposed to similar data breaches before, defines the seized data as non-sensitive internal business files, it has announced that approximately 400 people thought to be affected by the breach will be informed of the breach.
Therefore, in order not to be the target of similar security breaches that may be carried out in this context, it is recommended to consider the following practices and precautions:
- The system/program or software being used should always be kept up to date,
- Updates and fixes that eliminate vulnerabilities should be applied immediately,
- Institution/organization personnel should be made aware of possible social engineering/phishing attacks,
- Critical system/data should be backed up regularly,
- Comprehensive security solutions should be used,
- Passwords used in accounts should be created using strong policies,
- MFA/2FA authentication features should be enabled on all possible platforms,
- Attack surface analysis tests should be performed regularly in the institution/organization network.
In order not to be the target of similar ransomware attacks that may be carried out in this context, it is recommended to take the following actions;
- Beware of unreliable e-mail contents,
- Suspicious e-mail attachments and links should not be respected,
- Using reliable Anti-Malware solutions,
- Using licensed and up-to-date technologies,
- Used security solutions should block shared IOC findings regarding the malware campaign.
GitLab Releases Security Updates Fixing Critical Vulnerabilities
GitLab has released fixes and updates that fix critical vulnerabilities as part of the June security updates.
Some of the security vulnerabilities that have been fixed with the released updates and rated as critical, high, and medium are as follows;
- Vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-2185 (critical) exists due to incorrect input validation in Project Imports. As a result, a remote privileged user can import a maliciously crafted project, causing remote code execution on the vulnerable system.
- The XSS vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-2235 (high) is due to insufficient sanitization of user-supplied data in ZenTao integration. As a result, a remote threat actor can direct targets to open a specially crafted link and run arbitrary HTML and script code in the user’s browser in the context of the vulnerable website.
- The security vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-2229 (high) is caused by incorrect authorization. A remote threat actor can extract the value of an unprotected variable whose name it knows in public or private projects of which it is a member.
These vulnerabilities affected all GitLab CE/EE versions between 13.7.0 and 15.1.0 (inclusive) and were fixed in the released versions 15.1.1, 15.0.4, and 14.10.5. Users using vulnerable GitLab versions are advised to apply the released updates immediately.






