Critical Vulnerabilities Affecting 1000+ Organizations Detected in FileWave MDM Solution
Critical security vulnerabilities affecting more than a thousand organizations have been identified in the MDM (Mobile Device Management) solution of FileWave, which provides device management solutions based in Switzerland. Considering the widespread use of IoT technologies, it is observed that the use of device management solutions provided by FileWave is increasing day by day. The solutions make it easy for IT administrators to manage all of an organization’s devices effectively.
- The security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-34907, is due to an Authentication Bypass bug affecting FileWave MDM versions before 14.6.3 and 14.7.x, allowing threat actors to circumvent authentication mechanisms in the vulnerable system.
- A second vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-34906, is due to the presence of the hard-coded encryption key found in FileWave MDM versions before 14.6.3 and 14.7.x.
By exploiting the vulnerabilities, threat actors can capture critical data in the affected installations and execute arbitrary code on the system. Additionally, threat actors can use CVE-2022-34907 not only to hijack all managed devices but also to leak sensitive data such as device serial numbers, user email addresses, geolocation coordinates, IP addresses, device PINs, and more.
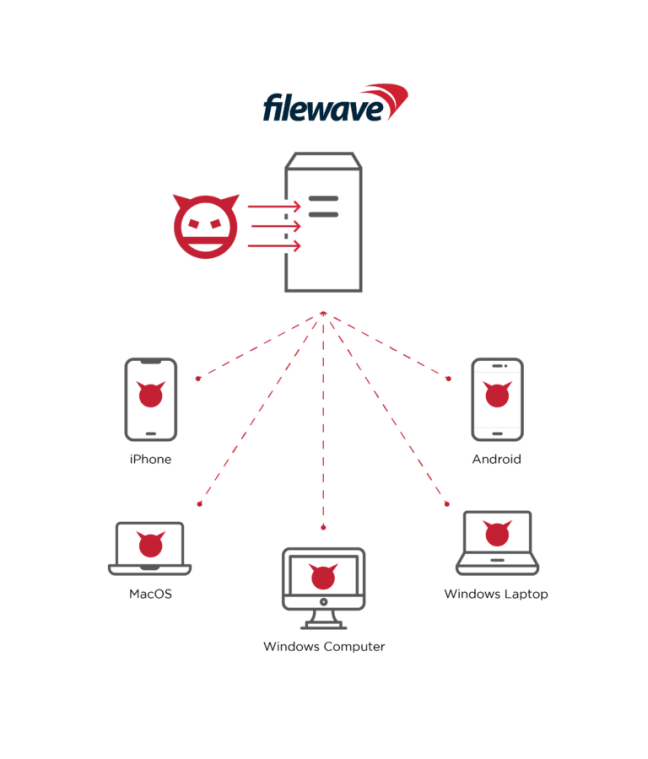
Vulnerable MDM installations are known to compromise the security of more than 1000 organizations. FileWave has fixed security vulnerabilities with a recent update (14.8). In this context, it is recommended that institutions/organizations or organizations using vulnerable MDM solutions immediately apply the security updates published in order not to be the target of attacks that can be carried out using vulnerabilities.
Critical Vulnerabilities Detected in Moxa NPort Series Devices
Two critical security vulnerabilities have been detected in the widely used NPort industrial connectivity appliance, manufactured by Taiwan-based industrial network and automation solutions provider Moxa, that could allow threat actors to disrupt systems.
0-day vulnerabilities tracked as CVE-2022-2043 and CVE-2022-2044 affect NPort 5110 device servers designed to connect devices to Ethernet networks. Remote threat actors can exploit security vulnerabilities to trigger a Denial of Service (DoS) condition on targeted devices. Exploiting both vulnerabilities requires network connectivity to the targeted device. Moxa has stated that the vulnerabilities only affect Firmware 2.10.
Affected NPort devices are widely used in many industries worldwide, including critical infrastructure sectors such as energy, manufacturing, and transportation systems. There are also allegations and reports that the devices in question were manipulated in 2015 attack campaigns targeting Ukraine’s electricity grid, which resulted in significant power outages. In this context, in order not to be the target of potential attacks that can be carried out by targeting critical infrastructure, it is recommended to consider the following practices:
- Network exposure for all control system devices or systems should be minimized and ensured that they are not accessed over the Internet.
- When remote access is required, secure methods such as a Virtual Private Network (VPN) should be used;
- Control systems should be isolated from other networks against external attacks,
- Comprehensive network and security solutions should be deployed,
- It should be ensured that the systems being used are using the most current version available.
0-Day Vulnerabilities in PrestaShop Makes E-Commerce Sites Vulnerable
Multiple critical 0-day security vulnerabilities which threat actors use to inject malicious code into e-commerce sites have been detected in the PrestaShop E-Commerce platform. The combined use of security vulnerabilities causes threat actors to remote code execution (RCE) on affected web servers and capture their customers’ payment information.
The attack requires the platform to be vulnerable to SQL injection exploits. In the analysis performed, the attack starts with the threat actors sending malicious GET and POST requests to the endpoint open to SQL injection. Then, threat actors gain full control via the PHP file created at the platform’s root directory and inject a fake payment form on the prepayment page. In this way, the credit card information entered in the fake form by the store customers is captured. Additionally, PrestaShop officials stated that threat actors might be using MySQL Smarty cache storage features as part of the attack vector. Therefore, it is recommended to disable this feature as a mitigation measure.
SQL injection vulnerabilities affect PrestaShop versions 1.6.0.10 or higher. 1.7.8.2 and higher versions are not affected by the security vulnerability in default configurations. PrestaShop 1.7.8.7 was released to harden MySQL Smarty cache storage against code injection attacks. Web application administrators using vulnerable PrestaShop versions must immediately apply the updates that fix the vulnerabilities.






