A Critical Data Disclosure Vulnerability Has Been Detected in Slack
Slack, an internal messaging and communication application for organizations/businesses, is vulnerable to a security vulnerability that exposes user credentials.
The vulnerability was detected in Slack’s “Shared Invite Link” component. The “Shared Invite Link” functionality allows workspace administrators to create links to include other participants in the workspace. With this feature, the personnel of the institution/organization are invited to become workspace members via e-mail. The detected security vulnerability causes the hash values of Slack passwords to be transmitted to other workspace members when a user creates an invitation link. These password hashes do not appear in any Slack client. Accessing password hashes requires active monitoring of encrypted network traffic from Slack’s servers.
The vulnerability affects all users who created or canceled an invite link between April 17, 2017, and July 17, 2022. Slack officials have announced that as a precaution against the potential risk of a data breach, affected users have reset their Slack passwords. Slack users must set a new Slack password to log in again.
In this context, it is recommended to create new passwords by applying strong and unique policies, to enable MFA/2FA authentication controls on all possible platforms as a precaution against similar security vulnerabilities that may cause data breaches, and to ensure that the applications/programs and systems being used are always up to date.
A New AiTM Phishing Campaign Targeting Institution/Organization Personnel Has Been Detected
A large-scale phishing campaign using advanced AiTM (Adversary in the Middle) techniques has been detected by ThreatLabz researchers. AiTM attacks are newer and more advanced phishing attacks in which user login and session cookies are compromised, and MFA/2FA authentication processes are circumvented. The detected new campaign targets end users in organizations using Microsoft’s e-mail services.
A phishing campaign begins with the delivery of e-mails containing a malicious link to targets. Threat actors create newly registered phishing domains to target users of Microsoft mail services. An HTML page is opened in the user’s browser when users open the malicious phishing URL in the phishing e-mail, which allegedly contains details about an incoming invoice. The HTML page uses the window.location.replace() function to redirect visitors to phishing pages controlled by threat actors. Using multiple URL redirection methods helps avoid the campaign’s detection by corporate e-mail URL analysis solutions.
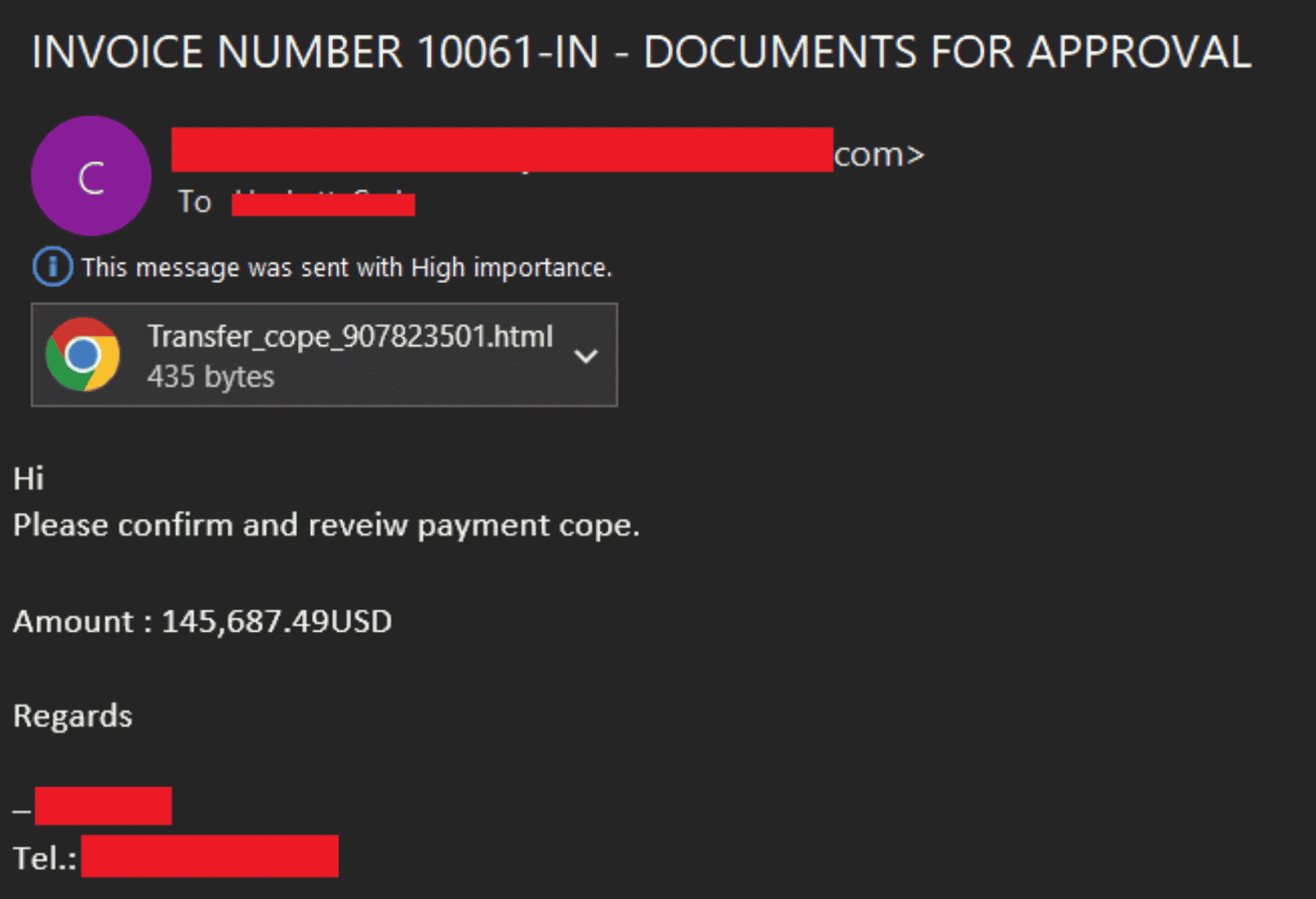
On phishing pages that appear as a Microsoft Office login page, the visitors’ MFA/2FA authentication processes are bypassed with advanced AiTM techniques, and user credentials are captured. There are three main open source AiTM phishing kits used in such attacks;
- Evilginx2
- Muraena
- Modlishka
In addition, abuse of legitimate online code editing services such as CodeSandbox and Glitch has also been observed to ensure the longevity of the campaign process. The campaign targets the FinTech, Finance, Insurance, Accounting, and Energy sectors, which generally provide services in the USA, England, New Zealand, and Australia. In addition, it has been observed that threat actors register domain names impersonating Federal Credit Unions outside of Microsoft.
Business e-mail security (BEC) remains an ever-present threat to organizations. The campaign underlines the importance of the need to protect against similar attacks, which are increasing day by day. In order not to be the target of similar advanced phishing attacks that may be carried out in this context, it is recommended to implement the following security measures.
- E-mails, attachments, and links from unknown and suspicious parties should not be respected,
- Sensitive information should not be used on platforms that are not sure of its reliability,
- Comprehensive Anti-Virus / Anti-Malware security solutions should be used,
- Institution/organization personnel should be made aware of potential phishing/social engineering attacks,
- Detected IOC findings related to the campaign should be blocked from security solutions.
Critical Vulnerabilities Affecting 1000+ Organizations Detected in FileWave MDM Solution
Critical security vulnerabilities affecting more than a thousand organizations have been identified in the MDM (Mobile Device Management) solution of FileWave, which provides device management solutions based in Switzerland. Considering the widespread use of IoT technologies, it is observed that the use of device management solutions provided by FileWave is increasing day by day. The solutions make it easy for IT administrators to manage all of an organization’s devices effectively.
- The security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-34907, is due to an Authentication Bypass bug affecting FileWave MDM versions before 14.6.3 and 14.7.x, allowing threat actors to circumvent authentication mechanisms in the vulnerable system.
- A second vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-34906, is due to the presence of the hard-coded encryption key found in FileWave MDM versions before 14.6.3 and 14.7.x.
By exploiting the vulnerabilities, threat actors can capture critical data in the affected installations and execute arbitrary code on the system. Additionally, threat actors can use CVE-2022-34907 not only to hijack all managed devices but also to leak sensitive data such as device serial numbers, user email addresses, geolocation coordinates, IP addresses, device PINs, and more.
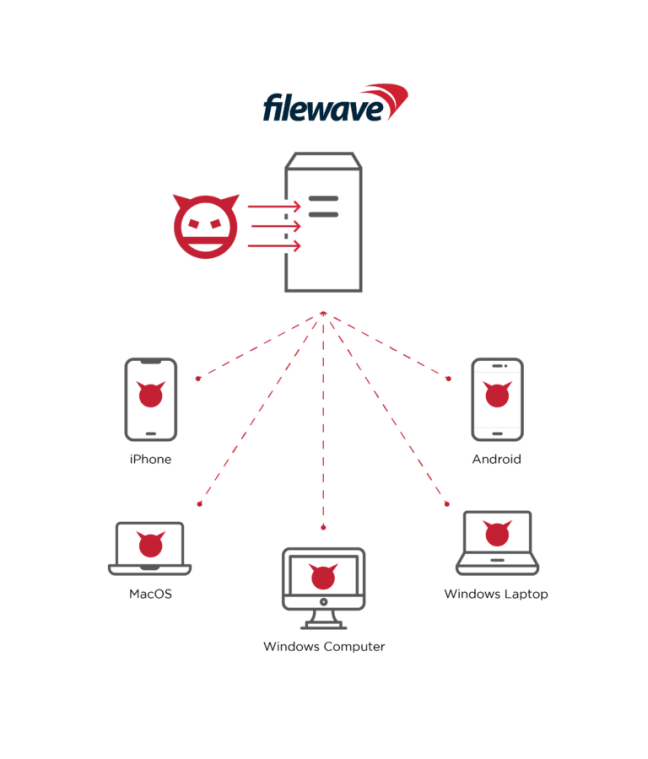
Vulnerable MDM installations are known to compromise the security of more than 1000 organizations. FileWave has fixed security vulnerabilities with a recent update (14.8). In this context, it is recommended that institutions/organizations or organizations using vulnerable MDM solutions immediately apply the security updates published in order not to be the target of attacks that can be carried out using vulnerabilities.






