TikTok Suffered A Data Breach Resulting In The Leak Of 2 Billion User Data
It has been detected that the source codes of the popular social media application TikTok and the sharing claiming that 2 Billion user data have been seized. The said data breach was claimed to be performed by the threat actor group known as AgainstTheWest, and screenshots of the allegedly seized data were shared on their social media accounts. It was stated in the post that the data breach occurred due to the use of weak passwords on the servers.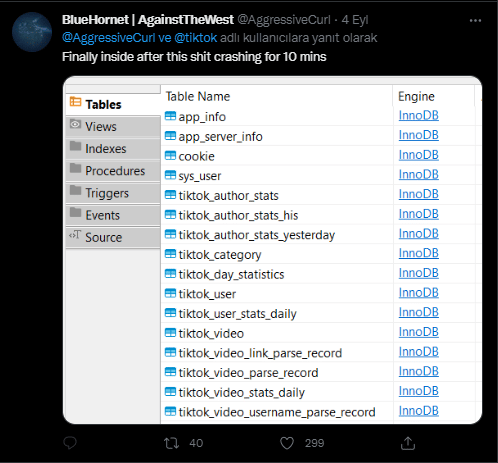
RedLine Stealer Malware Was Distributed Through the Corporate Social Media Accounts
Avast security researchers have identified multiple business accounts on social media that distribute the Redline Stealer malware, which is responsible for capturing users’ login credentials from infected systems.
The malware distribution campaign was identified through a sponsored post on Facebook promoting free Adobe Acrobat Reader software. The post in question was shared via the Facebook business account of Viu Internet, an internet service provider in Brazil. The post contains a link redirecting destinations to the “Mediafire.com” platform instead of “Adobe.com.” By clicking the link in the post, the files on the storage and sharing platforms are requested to be downloaded to the systems. Readline Stealer injection requires visitors to download the file, extract the content from the archive, and run it.

Viu Internet warns users who visit their homepage that their Facebook account has been hacked. In addition to Viu Internet’s Facebook account, several hacked Facebook business accounts have been found to post the same malicious content.
In this context, it is recommended to consider the following security warnings to avoid being the target of malware campaigns that can be carried out with similar methods.
- Emails, attachments, and links from unknown parties should not be respected.
- Advertisements and links in social media content should not be opened.
- Downloads of files, programs, or applications should be done from trusted, legitimate sources.
- Comprehensive security solutions (Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware) should be used.
MuddyWater APT Group Targeted the SysAid Servers
It has been determined that threat actors supported by Iran are carrying out attacks targeting vulnerable systems against the Log4j 2 vulnerability in Israeli institutions and organizations. The offensive campaign has been attributed to the MuddyWater (Cobalt Ulster, Mercury, Static Kitten) APT group known to be affiliated with the Iranian Ministry of Intelligence and Security (MOIS).
The attack vector begins with MuddyWater threat actors gaining initial access to systems by exploiting security vulnerabilities in SysAid servers. Based on observations from past campaigns by these threat actors and vulnerabilities found in target environments, the Microsoft security team has observed that the exploits are related to Log4j 2. In other attack campaigns observed in 2022, MuddyWater threat actors took advantage of Log4Shell vulnerabilities detected on VMware servers to gain initial access to systems. However, this campaign targeted SysAid servers, which are attractive to threat actors due to their widespread use in the targeted country and provide IT management tools for users.
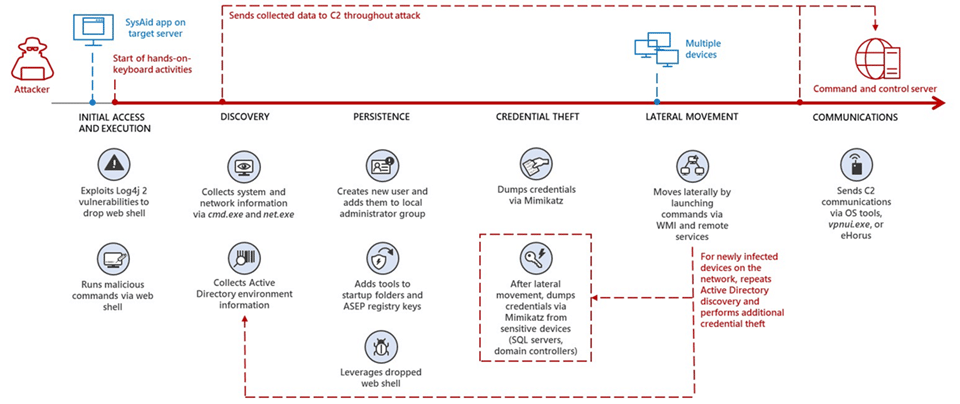
After gaining full access to target systems, threat actors capture critical and sensitive data from systems through Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) and hacking tools. In addition, it has been observed that threat actors benefit from WebShell malware for activities such as persistence in the targeted system, obtaining identity information, and lateral movement. Finally, a remote management tool called eHours is used for command and control (C&C) communication, which allows threat actors to monitor and manage targeted systems remotely.
Since it was announced, the Log4Shell vulnerability has been used in critical attacks targeting institutions/organizations. In this context, it is recommended to consider the following security practices to avoid the target of critical attacks that can be carried out using the said vulnerability.
- It should be ensured that the software, applications, and programs used are used in the current versions where the vulnerability has been fixed.
- Comprehensive security solutions must be deployed.
- Critical systems or data should be backed up regularly.
- IOC findings related to the attack should be blocked from the security solutions in use.






