American Airlines Suffered From A Data Breach
American Airlines suffered a security breach that compromised the security of customer and employee data. The security breach, detected by American Airlines on July 5, 2022, occurred when threat actors compromised the e-mail accounts of a certain number of employees.
There is no clear information about the data captured by the threat actors yet in this breach. However, it is considered that the said data may contain personal information such as name, surname, date of birth, e-mail address, telephone number, and driver’s license/passport number owned by employees and customers. In their statements, American Airlines officials stated that the data obtained through phishing attacks were not very large and a detailed investigation was launched into the breach, and no finding/evidence has yet been identified for the abuse of the seized data.
Additionally, American Airlines announced that it would provide customers affected by the breach with a 2-year subscription to Experian IdentityWorks, an anti-phishing solution. In this context, it is recommended that users who are at risk of being affected by the said security breach update the login information they use in their accounts by applying strong password policies, regularly reviewing their account activities, and being careful against target-oriented phishing / social engineering attacks.
Uber Suffered Extensive Security Breach, Resulting in Hijacking of Internal Systems
Uber suffered a wide-ranging security breach that compromised its internal systems and data by threat actors. Threat actors targeting Uber’s corporate infrastructure have posted images of evidence of the security breach. When the published screenshots are examined, it has been observed that the security of the following inventories used in Uber’s internal environment has been violated.
- Slack Server,
- Google Workspace Admin,
- AWS Accounts,
- HackerOne Admin,
- SentinelOne EDR,
- vSphere,
- Financial Dashboards
The attack vector starts with targeting MFA (Multi-factor Authentication) codes provided by Duo Security belonging to UBER employees. Although MFA authentication mechanisms can protect against a threat actor with the credentials of the targets, they are often vulnerable to MiTM attacks. Therefore, threat actors take advantage of this vulnerability to create phishing pages where they can capture the targets’ login credentials and MFA codes. These phishing pages are created using hacking tools such as Evilginx and mimic Uber’s login pages. With this method, threat actors seize the employee’s existing VPN access and use it to access the internal network. Threat actors gaining access to the internal network discovered an internal network share containing scripts with privileged credentials, allowing access to critical systems. Threat actors claim that they breached the security of Uber’s Duo, OneLogin, AWS, and GSuite environments with this attack chain.
In a screenshot released by the threat actors, it is observed that a SentinelOne EDR account belonging to Uber’s IR (Incident Response) personnel was also compromised. EDR solutions allow IR teams to access and control working machines, thus allowing threat actors to inject Backdoor-like malware into other internal systems, expanding the attack surface area in case of a security breach.
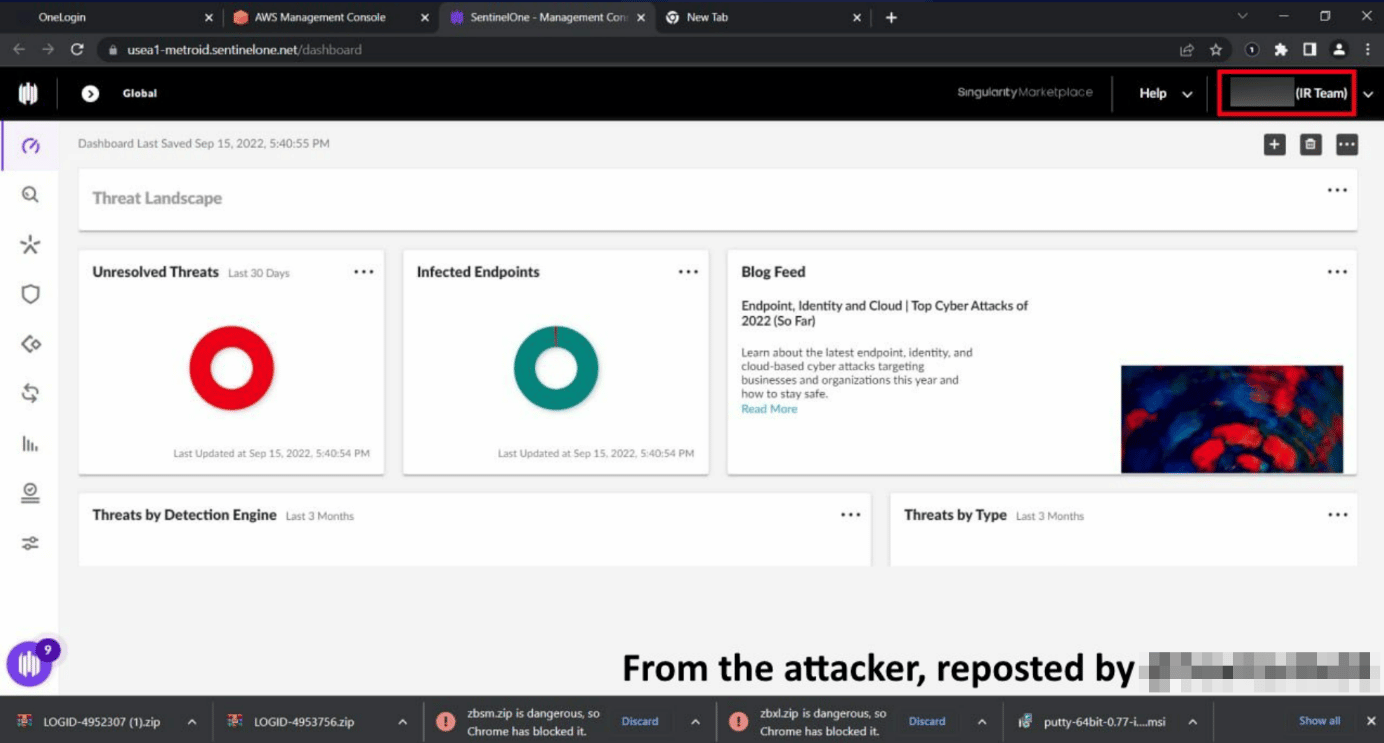
Uber stated on their social media accounts that they responded to the security breach in question, that they are in contact with law enforcement and will inform in case of any development. In this context, taking the following precautions into consideration is recommended to avoid being exposed to security breaches that can be carried out with similar techniques.
- Institution/organization personnel should be made aware of advanced target-oriented social engineering/phishing attacks that can be carried out.
- Critical data, such as login information, should not be used on unsafe platforms.
- It should be ensured that inventories such as the system, software/program, and application are used in the most up-to-date versions.
0-Day Vulnerability Detected in WPGateway Plugin
A critical 0-day vulnerability actively exploited by threat actors has been identified in the WPGateway plugin, which provides cloud service to WordPress users with installation, backup, and cloning capabilities.
The vulnerability, identified by WordFence security researchers and tracked with code CVE-2022-3180, allows an unauthenticated threat actor to add an administrator account to websites running WPGateway. As a result, threat actors with administrator privileges take full control of the site.
Using the vulnerability, more than 4.6 million attack attempts targeting more than 280,000 WordPress sites were detected and successfully blocked in the last month. The WordFence team has reported the vulnerability to WPGateway developers and has published a firewall rule for Wordfence Care/Wordfence Response customers. The most common observed security breach indicator for exploiting the vulnerability is the administrator account created with the “rangex” username. It was observed that the WPGateway plugin, last reviewed on September 9, is still vulnerable to vulnerability.
There is no update yet that fixes the vulnerability. In this context, in order not to be the target of attacks that can be carried out using vulnerabilities, it is recommended to follow the updates to be published regularly and to apply them immediately if they are published, to remove the installed WPGateway plugins until the update is released, and to check whether there are suspicious administrator users in the WordPress control panel.
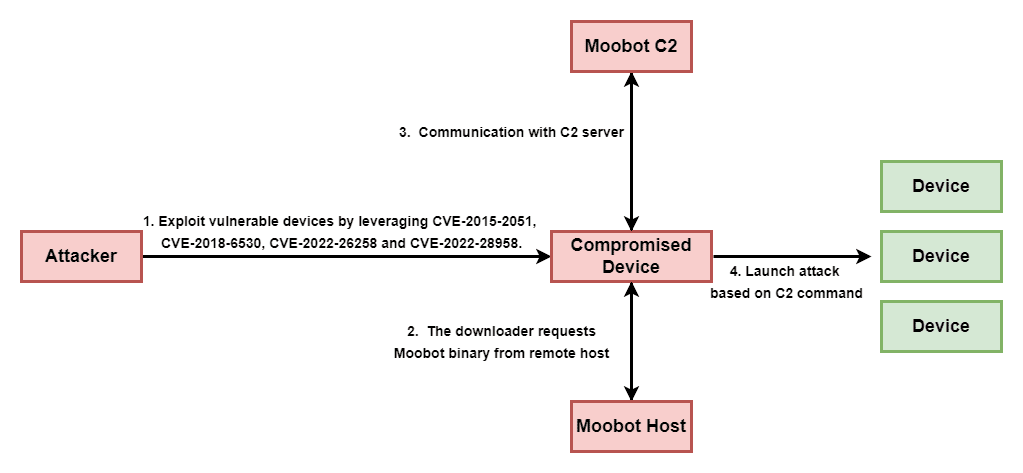
D-Link has released security updates regarding the specified security vulnerabilities, but still, many users are known to be running un-updated older versions or vulnerable devices. Therefore, in order not to be the target of similar malware attacks that may be carried out, users using vulnerable D-Link versions are recommended to apply updates that fix the vulnerabilities immediately. In addition, it is important to prevent the IOC findings related to the campaign in question from the security solutions in use.






