A New Android Banking Trojan Distributed via Google Play Store: “OCTO”
A new malware campaign has been detected deploying the banking trojan “OCTO”, which aims to hijack users’ banking information through multiple Android apps with more than 50,000 downloads on the Google Play Store. OCTO Trojan malware is a new variant of Exobot malware that targets financial institutions in various countries such as Turkey, France, Germany, Australia, Thailand, and Japan.
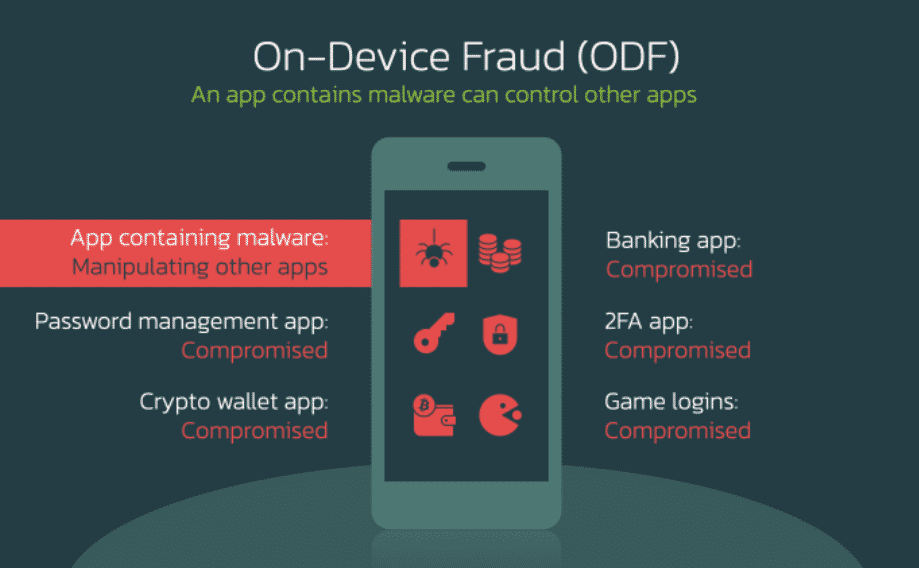
OCTO malware has many functions, such as recording keystrokes (keylogging), hijacking credentials, bypassing security solutions, and ensuring persistence on the target system. Also, Octo Malware gains remote access capability through the update to ExobotCompact, allowing threat actors to perform on-device fraud (ODF) activities.
ODF is a very dangerous, risky, and unsuspecting type of fraud transaction are started from the device the targets are using and can be used in other applications available in the system. However, performing such fraudulent activities on the target system requires users to enable Accessibility Services.
Applications used for the distribution of malware are as follows:
- Pocket Screencaster (Com.Moh.Screen)
- Fast Cleaner 2021 (Vizeeva.Fast.Cleaner)
- Play Store (Com.Restthe71)
- Postbank Security (Com.Carbuildz)
- Pocket Screencaster (Com.Cutthousandjs)
- BAWAG PSK Security (Com.Frontwonder2)
- Play Store App Install (Com.Theseeye5)
OCTO trojan distributed through the above applications can also be distributed via fake Google Chrome or Play Store updates. OCTO’s capabilities to capture screen contents in real-time and record keystrokes allow threat actors to capture entered credentials, a lock pattern or PIN code used to unlock the device, and user data stored in browsers.
Based on the different communication techniques established by OCTO with command and control (C&C) servers, multiple different threat actors are thought to be behind the attacks. It has been foreseen that attacks using malicious software with financial motivation such as OCTO, Cerberus, and Medusa will continue to increase.
To not be the target of similar campaigns, it is recommended to download applications/programs from reliable official sources, check the permissions requested by the applications, keep the applications downloaded to the devices to a minimum, and use Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware solutions.
Fake Web Apps Steal Android Users’ Banking Information
It has been detected that threat actors manipulate various Android applications and carry out campaigns targeting the banking information of Malaysian Android users.
The campaign begins with the web apps of cleaning services Grabmaid, Maria’s Cleaning, Maid4u, YourMaid, Maideasy, MaidACall, and a pet store PetsMore imitated by threat actors and delivered to their targets via Facebook ads. However, these fake web apps do not offer targets the option to make direct online purchases. Instead, targets are requested to download the relevant apps from the Google Play app store. However, the “Download” buttons provided for users to download the application via Google Play do not direct users to Google Play but to servers under the control of threat actors.
Successful execution of the campaign requires Android users to enable the “Install Unknown Apps” option on their devices. Additionally, it has been observed that some of the fake web applications in question do not have an Android application on Google Play, contrary to what is claimed.

Applications require users to login to appear legitimate after they are downloaded and launched; however, there is no account verification mechanism on the server-side. Apps with the appearance of a real e-store imitate the interface of the original stores, offering the option to order and pay for the goods and services purchased. The targets can pay by credit card or by transferring the required amount from their bank accounts at the next stage. Users who choose the direct transfer option are presented with a fake FPX checkout page and are asked to select their bank from among the eight Malaysian banks provided and then enter their credentials.
It has been observed that the targeted banks are Maybank, Affin Bank, Public Bank Berhad, CIMB Bank, BSN, RHB, Bank Islam Malaysia, and Hong Leong Bank operating in Malaysia. At the last stage, an error message is sent to the end-users that provide their banking information as input, stating that the username and password are invalid. As a result, the bank information entered by the user is captured by threat actors.
In order not to be the target of similar campaigns, should not respect advertisements observed on social media platforms, application downloads should be made through reliable application stores, the reliability of platforms where critical information is requested should be checked, 2FA / MFA features should be enabled on every possible platform.
The Critical Vulnerability in Elementor WordPress Plugin Affects Thousands of Websites
A critical remote code execution vulnerability has been detected in Elementor, the leading website building platform for WordPress, that could affect nearly 500,000 websites.
The exploitation of the vulnerability requires authentication, but it is a serious threat that anyone entering the vulnerable website, including regular subscribers, can take advantage of the vulnerability. A threat actor that creates a regular user account on an affected website can change the name and theme of the affected site to make it look completely different.
It is foreseen that an unauthenticated user too may exploit the critical vulnerability in the Elementor plugin in the continuing process. This RCE vulnerability has been fixed in the published version of 3.6.3. To avoid being affected by attacks that can be carried out using this vulnerability, website administrators are advised to apply the latest update available for the WordPress plugin or remove the plugin entirely from the website.
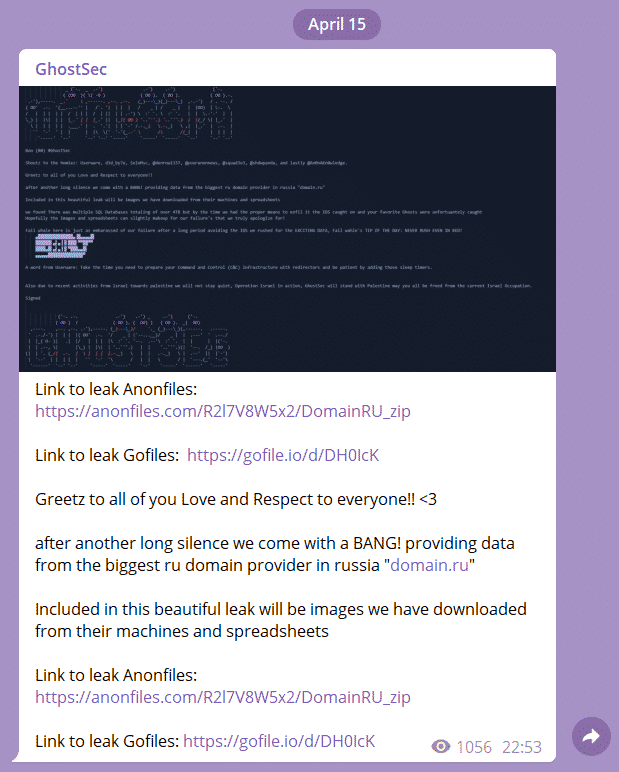
The Allegation that the Data of the Russian-Based Domain Registrar Domain.ru Was Captured
It has been detected that GhostSec threat actors have targeted Russian-based Domain registrar Domain.ru, and they have been posts claiming that critical corporate data has been compromised.
In the post, they published a ZIP archive containing images and spreadsheets of the threat actors allegedly belonging to Domain.ru. In the .md file called “Readme” added to the ZIP archive, it has been specified that attackers discovered multiple SQL files of 4TB during the attack, but the files could not be seized, and malicious requests were blocked by IDS (Intrusion Detection System) solutions. Sharing and proof images of the finding are given below: