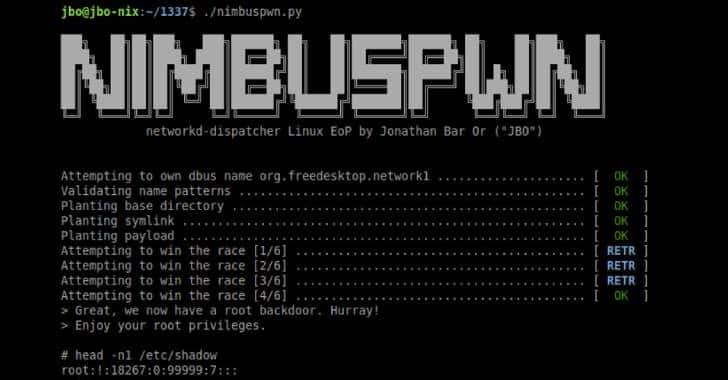
Multiple Privilege Escalation Vulnerabilities Detected in Linux Operating System
Microsoft security researchers have detected two critical vulnerabilities that could allow threat actors to carry out a series of malicious activities with root privileges on Linux systems. The vulnerabilities collectively called “Nimbuspwn” can be used to gain root privileges on Linux systems and allow threat actors to deploy various malicious software, such as backdoors and ransomware, to the vulnerable system.
Nimbuspwn security vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2022-29799 and CVE-2022-29800, exist in networkd-dispatcher, a component that sends link state changes on Linux machines. The vulnerability tracked as code CVE-2022-29799 exists due to a Directory Traversal error in the _run_hooks_for_state function in the source code of networkd-dispatcher. Another security vulnerability with code CVE-2022-29800 is related to a time-of-check to time-of-use (TOCTOU) error in the _run_hooks_for_state function.
Russia-based Energy Organization Elektrocentromontazh Targeted by Anonymous
It has been detected that Anonymous threat actors have shared a breach of the e-mail system security belonging to the Russian-based energy organization Elektrocentromontazh (EMC). Elektrocentromontazh provides electrical installation, transportation, manufacturing, design, and information technology services.
When the share was examined, it was observed that 1.23 million e-mails with a size of 1.7 TB, allegedly belonging to Elektrocentromontazh, were seized by threat actors and shared publicly in torrent file format. The sharing states that local ECM customers include important institutions/organizations such as Novovoronezh, Kursk, and Smolensk Nuclear plants, Moscow Electrical Directorate, the Moscow Government Energy Department, and Baltic oil Pipelines LLC. In addition, it is known that companies such as AREVA GmbH, Schneider Electric, and SIEMENS are among the international customers of ECM.

Frappo: A New “Phishing-as-a-Service” On The Dark Web
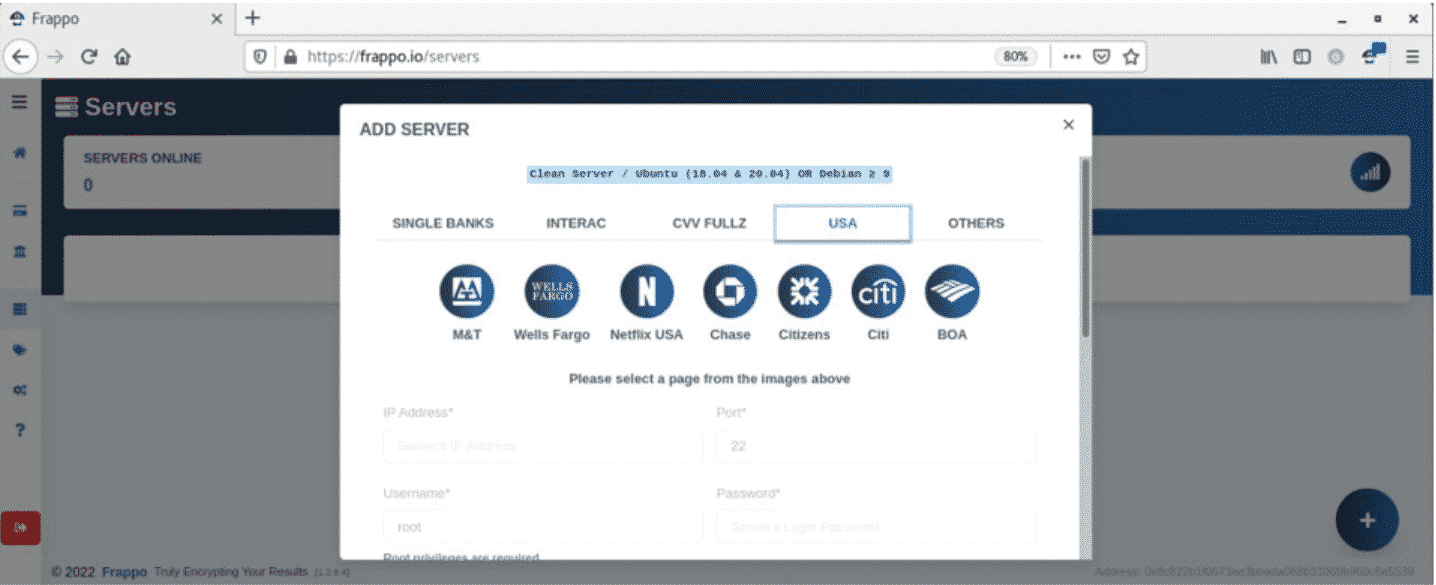
A new underground service called “Frappo” has been detected on the dark web by security researchers at Resecurity Hunter. Frappo provides threat actors with the ability to host and create high-quality phishing pages that imitate online banking, e-commerce, popular retailers, and online services to capture customer data.
Frappo is a service that serves as a Phishing (PaaS) provider as a Service. The service, first known to emerge on the dark web around 22 March 2021, has been significantly improved, providing phishing pages for more than 20 financial institutions, online retailers, and popular services such as Netflix and Uber. In terms of appearance, Frappo is designed as a service that gives the impression of an anonymous crypto wallet. The original project with a similar name is currently available on GitHub, allowing developers to integrate payment methods that support Ethereum and Bitcoin.

It was observed that Frappo, technically a browser extension, was added to Chrome’s online store by threat actors. Enabling the extension requires installing the browser plug-in on Firefox or Google Chrome and making payments.
Frappo developers offer a variety of payment plans for threat actors based on the subscription period they choose. When Frappo is activated, the threat actors are provided with a navigation menu to create a new phishing page (phishlet). An interactive wizard is then provided that allows threat actors to configure settings, define server credentials, and select the brand to imitate.
Phishing pages categorized by brand and profiles are of high quality and contain interactive scenarios that fool targets into entering critical credentials. Threat actors successfully use PaaS platforms such as Frappo for malicious activities such as Account Import (ATO), Commercial Email reconciliation (BEC), Payment, and Identity Theft.
Threat actors use advanced tools and tactics to target global consumers, so protecting digital identity becomes one of the most critical priorities for online security. In this context, it is recommended that;
- users and organizers who are members of e-commerce platforms ensure the reliability of the platforms where they use critical account information,
- do not rely on email, attachments, and links from unknown parties,
- not keep the input information available in the account in the browser memory,
- enable the 2FA/MFA features on any platform available, and
- use comprehensive security solutions.






