Microsoft Released Critical Security Updates
As part of the October security updates, Microsoft has released updates for 85 security vulnerabilities, including 0-day vulnerabilities known to be actively exploited by threat actors. The criticality ratings of the vulnerabilities are 15 critical, 69 high, and one medium. In addition, it is stated that the published updates do not cover the “ProxyNotShell” vulnerabilities (CVE-2022-41040, CVE-2022-41082) recently detected in Microsoft Exchange Server.
Some of the critical vulnerabilities fixed by the updates are as follows;
- The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-41033, is caused by a buffer overflow affecting the Windows COM+ Event System Service. The vulnerability, which affects all versions of Windows starting with Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008, allows a local user to execute code with SYSTEM privileges on a vulnerable system.
- The security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-37979, is caused by a Race Condition bug in Windows Hyper-V. A local user can exploit the vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information and elevate their privileges in the system.
- The security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-37976, is caused by improper enforcement of security restrictions in Active Directory Certificate Services.
- The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-37978, exists because the security features in Active Directory Certificate Services are bypassed. As a result, a remote user can exploit the vulnerability to perform man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks and gain access to network communications.
- The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-41043, exists due to excessive data output by Microsoft Office applications. As a result, a local user can gain unauthorized access to sensitive information in the system by exploiting the vulnerability.
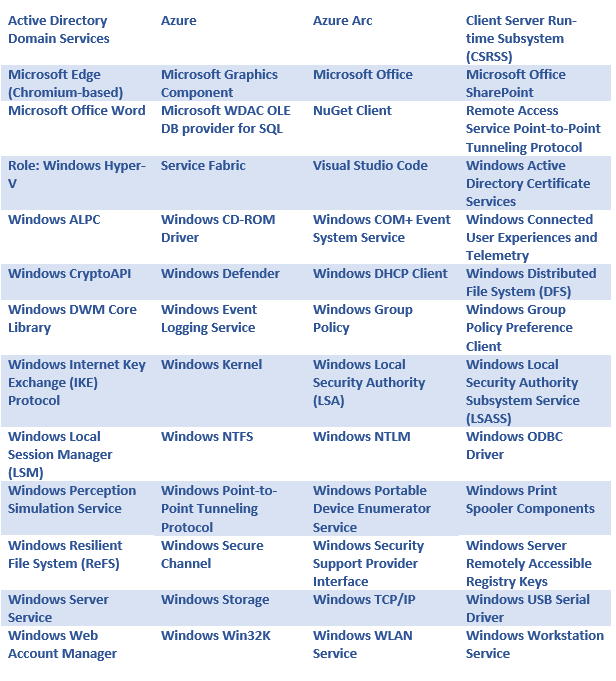
Updates that fix vulnerabilities affect the following Microsoft products and versions;
Toyota Confirms a Security Vulnerability Affecting Customer Data
Toyota has stated that a security vulnerability has been identified that compromises the 296,019 email addresses and customer management numbers of registered persons on the T-Connect help platform. T-Connect is a support platform for unlocking Toyota vehicles that offers features such as smartphone-based digital keys, navigation services, and remote start.
The vulnerability is due to a developer tasked with building the T-Connect platform uploading the site’s source code to a GitHub public repository in December 2017. Upon inspection of the publicly available source code by Toyota officials, it was discovered that the source code contained an access key to a server that stores customer data. Immediately after the vulnerable GitHub repository was discovered, Toyota officials made it private, and the exposed access key was replaced.
Toyota has launched an investigation into the vulnerability, but there is no evidence yet whether threat actors used the vulnerability to capture data from the server. It is recommended that T-Connect users with the potential to be affected by the breach be aware of the data that may be leaked to the internet regarding spear-phishing/Social engineering attacks and change the login information registered to the platform by applying strong password policies.
More than 400 Mobile Apps Detected to Hijack Facebook Login Credentials
More than 400 malicious Android and iOS apps have been identified by meta security researchers on the official Apple and Google app stores, aiming to hijack Facebook users’ login information. It has been observed that these malicious applications are disguised as photo editors, games, VPN services, business applications, and other utilities.
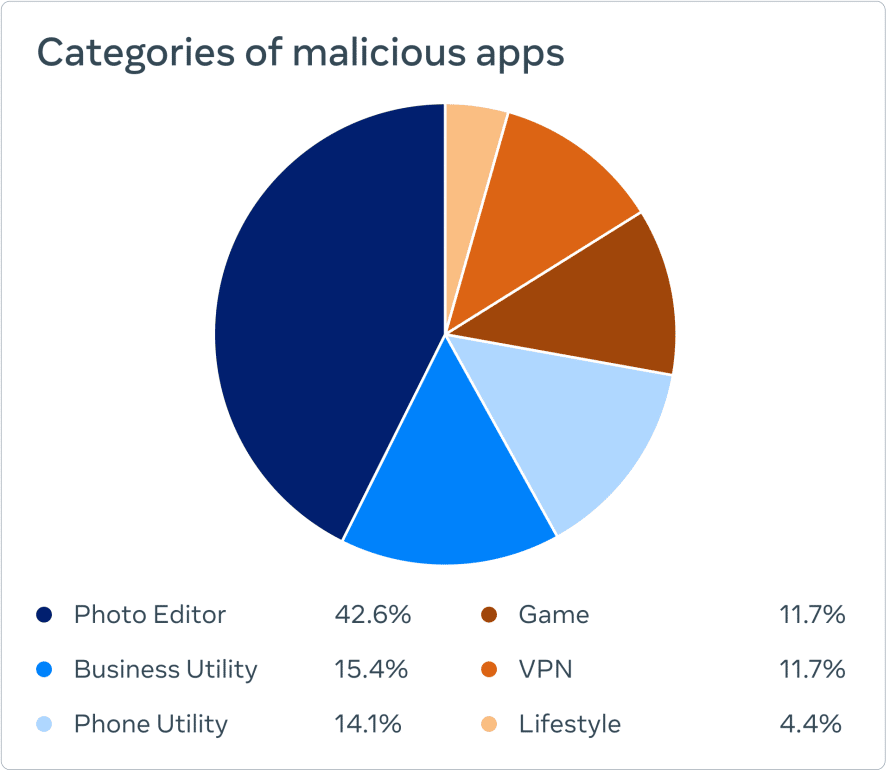
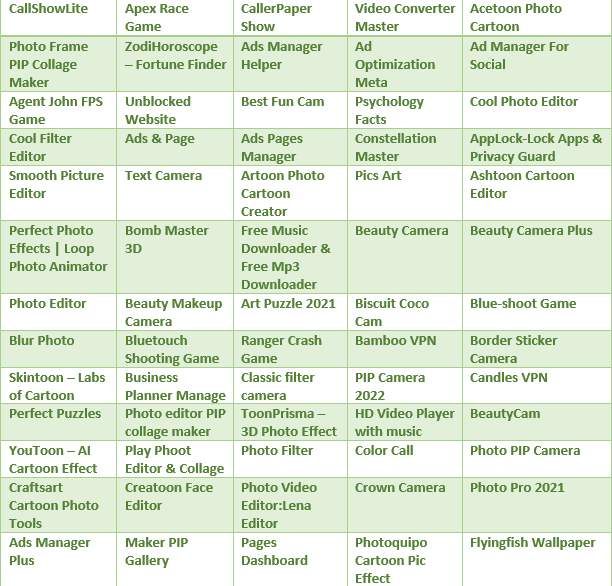
There are also many legitimate apps that offer the features listed above and require you to securely log into Facebook. In order to distinguish malicious apps from legitimate apps, there are a few important things to consider before logging into a mobile app with your Facebook account;
- If social media credentials are requested to use the application, it is important for users to check whether the application can be used without providing their Facebook information. For example, a photo editing app that requires your Facebook login and password before allowing you to use it has the potential to be harmful.
- App reputation, though imprecise, provides insight into whether the app is malicious before it is downloaded. Therefore, app reviews, downloads, and ratings, including negative ones, should be checked.
- It should be checked whether the application provides the promised functionality before or after login.
Considering these issues, users who suspect they have been affected by a malicious mobile application with the above features should take the following steps immediately.
- The app should uninstall from the device.
- Login information of social media accounts used in the application should be changed by applying strong password policies.
- Two-factor authentication mechanisms must be enabled.
- Login alerts should be enabled to detect unauthorized access attempts by unknown parties.






