How to Detect Phishing Emails?
Phishing is swindling people to gather the account credentials of a specific website, credit card details, and strategic information of their company, infecting computers for botnet attacks. Proactive and reactive protections against adversaries are not always sufficient since scammers target people who do not know how to protect themselves. Companies try to educate their employees to avoid being hacked.
So, how to detect phishing emails? Here are quick tips for identifying phishing email attacks.
Public Domain Names
@gmail.com, @outlook.com, and @hotmail.com are public domain names. Corporate email accounts do not use these domain names. Corporate email accounts have their unique domain name, such as @prismacsi.org. Public domain names generally belong to personal email accounts. If you see an email from a public domain name, but the content is like an email from a corporation, it might be a phishing attack.
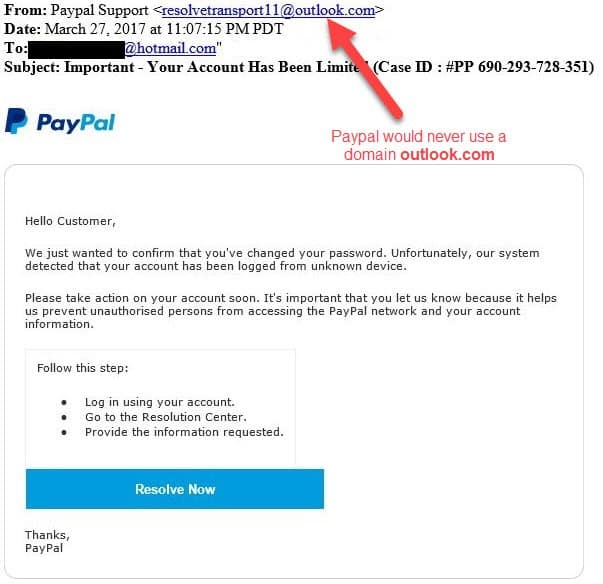
Misspelled Domain Names
Scammers may want to send an email from an account that does not have a public domain name. They may try to imitate the company to be more convincing.

Directing to the Login Page
If the email wants you to log in via a link, you should suspect that email. Most of the companies do not offer you to log in via a link because it is suspicious. You should go to that website from a new tab and log in from there.
Poorly Written Emails
Scammers might not be native English speakers. Therefore, there could be some typos. It does not always be mistaken letters. Grammatical errors also cause suspicion. If you see a typo or a grammatical error in an email, look for other evidence to prove the email is a lure.

Uncommon Phrases From Known People
If you have emailed a specific person for a while, you probably know their template of writing (e.g., salutation and valediction). If there is uncommon writing, you should suspect that email.
If the salutation does not contain your name (e.g., Dear Customer, Dear Account Holder, etc.), it must be sent to a lot of receivers. This is suspicious.
Suspicious Attachments and Links
Do not open the attachment unless you are sure that the source is legitimate. Also, do not open the extensions’ attachments: .exe and .zip. Otherwise, the attachment may contain malware and infect your machine. Moreover, an infection may spread to other computers connected to the same network. Infection can get login credentials, credit card details, or company-related information.
Legitimate companies do not send you attachments; they generally direct you to their website, and you can find the document there.
Scammers hide the links with buttons or short links. When you hover your mouse over the link/button, the exact address will appear on the right bottom of your browser. You can check the original address. If you use a mobile device, hold down on the link, and the original link will appear as a pop-up.

It is beneficial to care if the link starts with HTTPS. HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP. It encrypts the data traveling over the internet. If the link begins with HTTPS, it is hard to read the request and response between the client and server.
Creating Urgency
Scammers create a fake urgency so that you do not have time to think if that email came from a legitimate address. Here is an example of such an email.

Employees could be shy about verifying the email, especially if it comes from their boss. Companies should understand the reason why their employee request verification, and sometimes, they should even congratulate their employee for their caution.
Awards and Gifts
Another suspicious email content is that scammers might want you to believe that you gained an award. There would be a link to gather the award, but it is probably dangerous. Do not rush into getting the award.
There could also be gifts that some marketing companies offer you. These fake awards and gifts try to make you surprised so that you will not suspect them.
Do not forget! Scammers are likely to make you surprised or feared so that you will not have time to suspect them.
Signatures
Some companies’ employees have a specific signature that indicates that the email is coming from a legitimate source. If the signature is different or does not exist at all, there must be something suspicious. Contact that person to verify the email source.
What to Do with Suspicious Emails?
In today’s digital age, suspicious emails are an unfortunate reality that many of us face. These emails often contain phishing scams designed to steal personal and sensitive information. In general, this sensitive data consists of components such as credit card information and mail account passwords. You may experience material or moral damages with this stolen data. To protect yourself from these attacks, you must know phishing email detection techniques and implement best practices to prevent cyber attacks.
Phishing email detection involves recognizing the telltale signs of a fraudulent email. For example, phishing emails may contain requests for personal information, urgent messages that demand immediate action, or suspicious links or attachments. To avoid these scams, it’s crucial for employees to be aware of the red flags and follow some phishing tips.
First and foremost, employees should be aware of the risks associated with phishing attacks. Educating employees on phishing awareness tips, such as avoiding clicking on suspicious links or opening suspicious attachments and reporting any suspicious emails to the IT department, is essential.
Employees should forward the email to the IT department or the company’s phishing monitoring service to report phishing emails. Phishing monitoring involves continuously monitoring emails and identifying potential phishing scams to prevent cyber attacks.
Digital Risk Protection Services and Threat Intelligence Services are two options for companies looking to enhance their phishing email detection and prevention capabilities. These services can help companies identify and respond to potential threats, provide employee training and support, and implement best practices to prevent cyber attacks.
How to Avoid Phishing Emails?
The first step in avoiding phishing emails is understanding how to detect them. Phishing email detection involves identifying the characteristics of a suspicious email, such as the sender’s address, the tone of the message, and any links or attachments. You can also look for phishing tips for employees and phishing awareness tips to help you recognize these emails.
Phishing awareness tips can help you avoid phishing emails by teaching you to be cautious when opening emails from unknown senders or messages that seem too good to be true. Some common phishing awareness tips include avoiding clicking on suspicious links, never opening attachments from unknown senders, and checking the sender’s email address for accuracy.
Another way to avoid phishing emails is to report them to the relevant authorities. Reporting phishing emails to the IT department, the company’s phishing monitoring service, or law enforcement agencies can help prevent others from falling victim to the same scam.
Phishing monitoring is another essential tool for avoiding phishing emails. This involves monitoring your email account for potential phishing scams and blocking them before they can cause any damage. Digital Risk Protection Services and Threat Intelligence Services are two options for companies looking to enhance their phishing monitoring capabilities.
Digital Risk Protection Services and Threat Intelligence Services can help businesses protect themselves from phishing emails by providing employee training and support, identifying potential threats, and implementing best practices to prevent cyber attacks.
In summary, phishing emails significantly threaten your personal and financial information. However, by understanding how to detect them, following phishing tips for employees and phishing awareness tips, reporting suspicious emails, and leveraging phishing monitoring services like Digital Risk Protection and Threat Intelligence, you can avoid phishing scams and protect yourself from cyber-attacks.
Sources
https://www.securitymetrics.com/blog/7-ways-recognize-phishing-email
https://webcomsolutions.com.au/how-to-spot-a-scam-email/
https://umbrella.cisco.com/blog/grammar-and-spelling-errors-in-phishing-and-malware

