WhatsApp Suffered from a Data Breach – 487 Million Users’ Data in Danger
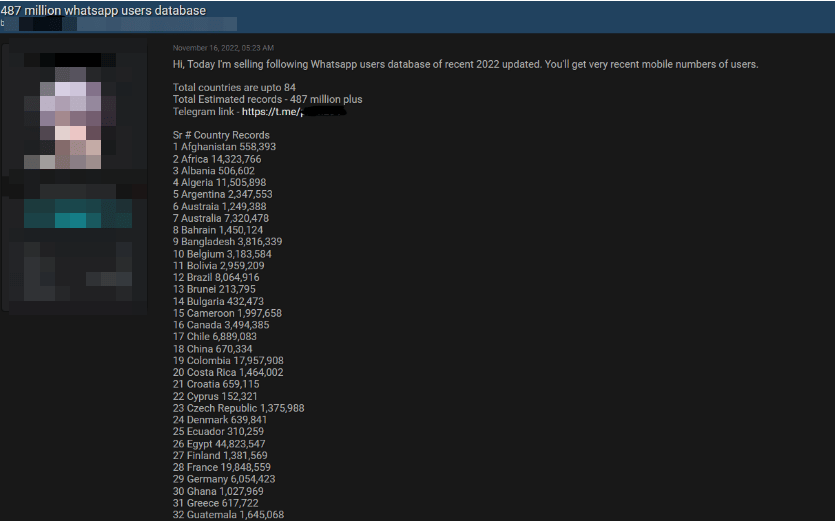
It is claimed that the database seized in the post contains the personal data of WhatsApp users from 84 countries. The distribution of the compromised data by country is given below;
- 45 Million User Data of Egyptian Citizens
- 32 Million User Data of US citizens
- 35 Million User Data of Italian citizens
- 29 Million User Data of Saudi Arabian Citizens
- 20 Million User Data of French Citizens
- 20 Million User Data of Turkish Citizens
- 10 Million User Data of Russian Citizens
- Over 11 Million User Data of UK Citizens
Cybernews researchers contacted the threat actor who shared the post and requested a data set sample as evidence to confirm the relevant leak. In the shared example, there are phone numbers of 1097 UK and 817 US users. However, the threat actor did not provide details on how the database was obtained, suggesting that they used their strategies to collect the data. Upon this, the analysis of the sample data set by Cybernews researchers confirmed that all numbers belong to active WhatsApp users.
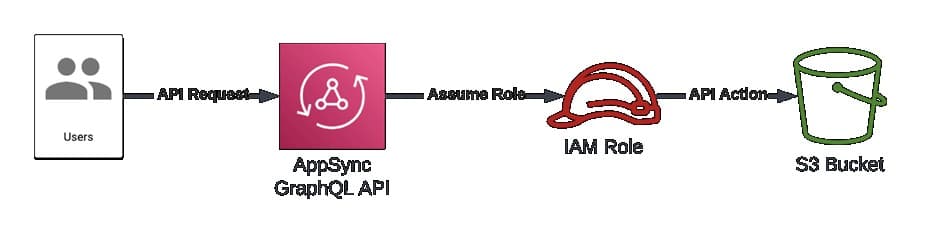
Amazon Fixes a Security Vulnerability Affecting AWS AppSync
A security vulnerability called “cross-tenant” has been detected by Datadog researchers in AppSync, a popular Amazon Web Services (AWS) tool. AppSync is a popular AWS service that allows developers to quickly create GraphQL and Pub/Sub APIs.
The vulnerability is due to a case-sensitivity parsing issue of the AppSync service that could potentially be used to bypass cross-account role usage validations and act as a service on customer accounts. Successful vulnerability exploitation allows threat actors to assume Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles in other AWS accounts.
Multiple Vulnerabilities Detected in IT Management Solution GLPI
Multiple security vulnerabilities have been identified in GLPI, an open-source web application that helps institutions/organizations and companies manage their IT infrastructure and inventories. These vulnerabilities allow threat actors to execute SQL queries against the application database and to perform Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) attacks.
The details of the detected security vulnerabilities are as follows;
- The security vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-39375 is due to insufficient cleaning of user-supplied entries in the RSS Feed function. A remote threat actor can execute arbitrary HTML code and script in the user’s browser in the context of the vulnerable website via a malicious link. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows remote threat actors to obtain sensitive information, alter the web page’s appearance, and carry out phishing attacks.
- The security vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-39234 is due to an insufficient session expiration time. This vulnerability allows threat actors to access users’ accounts by reusing users’ old session credentials (Cookies) and thus may lead to the capture of users’ sensitive information.
- The security vulnerability tracked as CVE-2022-39323 is due to insufficient sanitization of user-supplied data in the API REST user_token component. A remote threat actor can execute arbitrary SQL commands in the application database by sending a specially crafted request to the affected application.
- The security vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-39276, is due to insufficient validation of user-supplied inputs in RSS feeds. A remote threat actor can direct the application to initiate requests to arbitrary systems (SSRF) via a specially crafted HTTP request.
- The vulnerability security tracked as CVE-2022-39277, is due to insufficient sanitization of user-supplied data on external connections. A remote threat actor can run arbitrary HTML code and script in the user’s browser in the context of the vulnerable website via a specially crafted link.
These vulnerabilities affect specific versions of GLPI, and security updates have been released that fix the vulnerabilities. In this context, it is recommended to immediately upgrade vulnerable installations to the current versions published in order not to be the target of attacks that can be carried out using vulnerabilities.






