Introduction
Malware, short for malicious software, is any software designed to harm or exploit computer systems. This can include viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and other types of malicious code. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number and sophistication of malware attacks. This has led to a growing concern about the security of computer systems and the need to protect against these threats.
Vulnerabilities, on the other hand, refer to weaknesses in software or systems that can be exploited by attackers. These can include defects in programming code, configuration errors, and other types of bugs. As with malware, there has been a significant increase in the number and sophistication of vulnerabilities found in software and systems in recent years. This has led to a growing concern about the security of computer systems and the need to address these vulnerabilities to protect against attacks.
It is becoming more challenging to ensure the security of our systems and protect our data with the continuous increase of advanced malware and the detection of new critical security vulnerabilities every second. Threat actors can exploit these currently detected vulnerabilities to obtain our sensitive data through advanced malware.
In our blog post, we described some of the vulnerabilities and malware we saw during 2022.
What is Vulnerability?
Vulnerability refers to a weakness or gap in a computer program or system that could be exploited by an attacker. These weaknesses can be caused by a variety of factors, such as poor coding practices, lack of input validation, or failure to properly handle sensitive data. Once a vulnerability is discovered, an attacker can use it to gain unauthorized access to a system, steal or corrupt data, or even launch a full-scale attack on the network.
Examples of common types of software vulnerabilities include:
- Buffer overflow: A buffer overflow occurs when a program attempts to store more data in a buffer than it can hold, causing the data to overflow into adjacent memory locations. This can be used to execute arbitrary code.
- SQL injection: SQL injection occurs when an attacker is able to insert malicious SQL code into a query, allowing them to gain access to sensitive data or execute arbitrary commands on the database.
- Cross-site scripting (XSS): XSS occurs when an attacker is able to inject malicious code into a web page viewed by other users, allowing them to steal sensitive information or execute arbitrary code on the user’s browser.
It’s important for software developers and system administrators to regularly check for and patch vulnerabilities in their systems and to have an incident response plan in case a vulnerability is exploited.
Vulnerability Trends
Security vulnerabilities detected in software and hardware are frequently used by threat actors to infect systems with malware, access sensitive information, and disrupt systems. Today, many institutions and organizations have a large number of unpatched vulnerabilities in their systems, providing threat actors with numerous attack paths. Every day, new security vulnerabilities are identified, and many of them can be exploited for years. In 2022, some of the security vulnerabilities that are frequently exploited by threat actors were as follows;
Log4Shell (CVE-2021-44228)
Log4Shell (CVE-2021-44228), identified in December 2021, is a critical vulnerability that allows for remote code execution on systems using Apache Foundation’s Log4j, an open-source Java library widely used in commercial and open-source software products and utilities.
Follina (CVE-2022-30190)
Follina (CVE-2022-30190), identified in June 2022, is a zero-day vulnerability that allows threat actors to execute code on targeted Windows systems through Microsoft Office documents.
Follina: The Critical 0-Day vulnerability Affects Windows Systems
Spring4Shell (CVE-2022-22965)
The Spring4Shell (CVE-2022-22965) vulnerability, identified in March 2022 in Spring (a popular Java-based web application framework), is a remote code execution vulnerability that results from the ability to pass user-controlled values to various properties of Spring’s ClassLoader. This vulnerability can be exploited by unauthenticated threat actors to inject a web shell and gain remote code execution.
Google Chrome Zero-Day (CVE-2022-0609)
The vulnerability in the Google Chrome web browser, tracked as CVE-2022-0609, identified in February 2022, allows threat actors to execute code on the user’s system by redirecting them to a malicious website. This vulnerability is known to be exploited by multiple hacking groups associated with the North Korean state-sponsored hacking group Lazarus.
Google Releases Updates to Actively Exploited 0-Day Security Vulnerability in Chrome
F5 BIG-IP (CVE-2022-1388)
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-1388, detected in May 2022 on F5 BIG-IP network devices (used for load balancing and other purposes), allows unauthenticated threat actors to execute commands on vulnerable devices by sending special requests.
Critical RCE Vulnerabilities Affecting F5 Products Detected
ProxyNotShell (CVE-2022-41082, CVE-2022-41040)
The vulnerabilities identified in September 2022 affect Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, 2016, and 2019 products. The critical vulnerability (SSRF), tracked as CVE-2022-41040, is caused by insufficient validation of user-supplied input in the Exchange OWA interface, allowing threat actors to direct the application to initiate requests to arbitrary systems via a specially crafted HTTP request. Another vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-41082, results from incorrect login validation in Exchange Server, allowing a remote user with access to PowerShell Remoting on Exchange systems to execute arbitrary code on the system. These vulnerabilities are known to be used in a chained manner by threat actors.
ZeroBot: New Botnet Malware Using IoT Security Vulnerabilities
Zimbra Collaboration Suite Bugs (CVE-2022-27925, CVE-2022-41352)
Security vulnerabilities identified in Zimbra Collaboration Suite, a popular platform for email, calendaring, and other collaboration services, allow threat actors to execute arbitrary commands on the server by sending a malicious request.
Atlassian Confluence RCE Flaw (CVE-2022-26134)
The vulnerability, identified in June 2022, is an unauthenticated OGNL injection remote code execution vulnerability affecting Confluence Server and Data Center versions later than 1.3.0. Threat actors can send a malicious HTTP GET request with an OGNL payload in the URI to exploit a vulnerable server. When this vulnerability is exploited, threat actors can execute remote commands with the privileges of the user running the Confluence application.
Zyxel RCE Vulnerability (CVE-2022-30525)
The vulnerability, identified in June 2022, affects Zyxel network devices and allows unauthenticated threat actors to inject commands into the operating system through the administrative HTTP interface of firewalls. This allows them to modify specific files and execute operating system commands.
Proxyshell (CVE-2021-31027, CVE-2021-34473, CVE-2021-34523)
ProxyShell consists of three separate flaws in the Microsoft Exchange email server that allow for bypassing security features, achieving remote code execution, and escalating privileges. When these vulnerabilities are combined on vulnerable systems, ProxyShell allows an attacker to establish persistence and execute malicious PowerShell commands. A successful exploit allows threat actors to gain full control of vulnerable Microsoft Exchange email servers.
How Can Brandefense Help You Against Vulnerabilities?
Vulnerability intelligence gives information about known vulnerabilities targeting software and systems, including information about the risk level, affected products, and discussions on social media. Vulnerability patches or workarounds that are available can be found with official references. It is used to help organizations identify and prioritize destructive vulnerabilities in both internal and external systems to develop strategies for mitigating dangerous risks.
Brandefense is a proactive digital risk protection solution for organizations. Our AI-driven technology constantly scans the online world, including the dark, deep, and surface web, to discover unknown events, automatically prioritize risks and deliver actionable intelligence you can use instantly to improve security. Our proactive approach enables you to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities in your systems and develop strategies for mitigating those risks.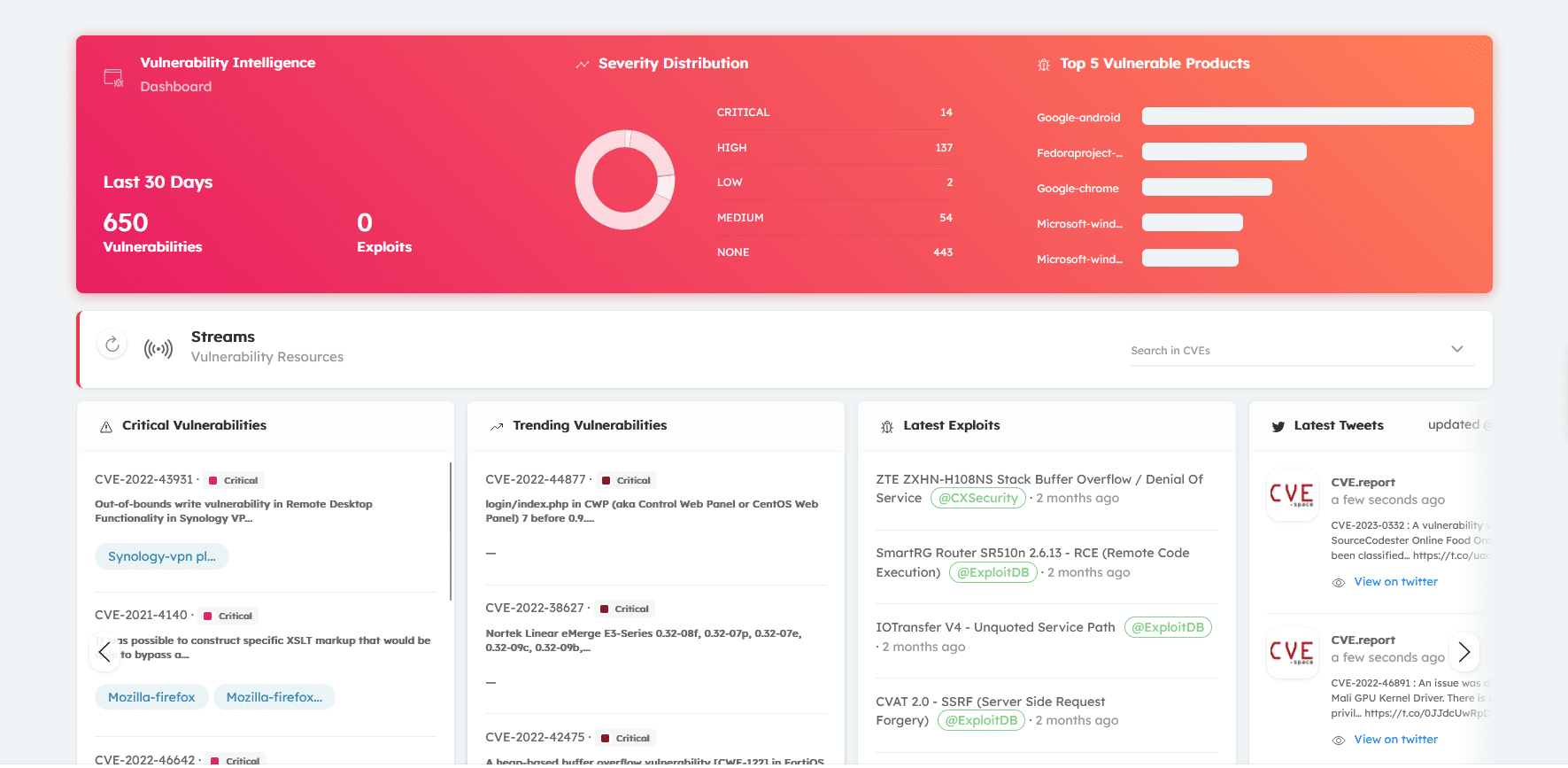
What is Malware?
Malware, short for “malicious software,” is any software or program that is designed to harm or exploit computer systems and networks. It can come in many forms, including viruses, worms, trojan horses, ransomware, and spyware. These types of software are typically created and distributed by cybercriminals with the intent of causing damage to a computer’s files, stealing personal information, or even taking control of a computer remotely.
Viruses are one of the most well-known forms of malware. They are designed to replicate and spread from one computer to another, often through email attachments or infected files shared on networks. Once a virus infects a computer, it can cause damage by deleting files or corrupting data, and it can also spread to other computers on the same network.
Trojan horses, often called simply Trojans, are malware that disguises itself as legitimate software. They can be distributed through email attachments, instant messaging, or downloaded from the internet. Once installed, they can give cybercriminals access to a user’s computer, allowing them to steal personal information, or even take control of the computer remotely.
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a user’s files and demands payment to restore access. Once a computer is infected with ransomware, the user will not be able to access their files until a ransom is paid. This type of malware is particularly dangerous because it can cause irreparable damage to a user’s files, and it can also be spread quickly through networks.
The best way to protect against malware is to use anti-malware software, keep software and operating systems up-to-date, and be cautious when opening email attachments or clicking on links from unknown sources.
Malware Trends
Malware is frequently used by threat actors to damage or exploit targeted computer systems, networks, or devices. Malware can be spread through various means, such as email attachments, infected websites, and online ads. It is known that threat actors are continuously developing more advanced versions of malware. In 2022, it was known that threat actors have utilized various advanced malware families for their purposes. Some of the malware families that were distributed to targeted systems in 2022 include;
European Focused Threat Actors – Ransomware Groups
Trickbot
First detected as a banking Trojan in 2016, Trickbot has been made more powerful through ongoing updates by threat actors and is delivered through the malware-as-a-service (MaaS) model. It is distributed through malicious links and attachments provided in spear phishing attacks. Trickbot is capable of stealing login credentials, collecting personally identifiable information, spreading malware across the network, and disabling Windows Defender’s real-time monitoring. It is also known to be used by threat actors to distribute ransomware, such as Ryuk and Conti.
Emotet
Emotet was first developed in 2014 as a banking Trojan and was discovered when customers of German and Austrian banks were infected. Through updates by threat actors, Emotet was transformed from a banking Trojan into a Trojan called a software installer that installs malware on devices. The malware is distributed via phishing emails, and once it gains access to targeted systems, it steals sensitive private data and tries to spread it to other computers on the network like a computer worm. In addition, Emotet is also able to trick and evade basic antivirus programs.
Initial Access Methods: How Malicious Actors Do Infiltrate Companies?
Qakbot
First identified as a credential stealer in 2008, Qakbot (also known as Qbot) has been developed into a modular second-stage malware with backdoor capabilities. Classified as a banking trojan, worm, and remote access trojan (RAT), Qakbot steals sensitive data and attempts to self-propagate to other systems on the network. It also provides remote code execution (RCE) capabilities, allowing attackers to perform manual attacks to achieve secondary objectives, such as scanning the compromised network or injecting ransomware. Qakbot is known to be used by apex ransomware gangs such as REvil, ProLock, and Lockbit to distribute ransomware.
Bitdefender Releases Decryptor for MegaCortex
Agent Tesla
Detected in 2014, Agent Tesla is a .Net-based remote access trojan (RAT) often used for malware-as-a-service (MaaS) and data stealing to gain initial access. As first-stage malware, Agent Tesla provides remote access to a compromised system, which is then used to download more sophisticated second-stage tools, including ransomware. Threat actors distribute Agent Tesla malware via phishing email campaigns as .zip, .gz, .cab, .msi, and .img files and as attachments to Microsoft Office documents containing malicious Visual Basic application (VBA) macros
APT Groups Actively Involved during the Russia-Ukraine Cyber War
RedLine Stealer
RedLine malware is a stealer that is distributed as cracked games, applications, and services. It aims to obtain data from web browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, and applications such as FileZilla, Discord, Steam, Telegram, and VPN clients. The malware is also known to send obtained data, such as running processes, security solutions, installed applications, Windows product names, processor architecture, etc., to the command and control (C2) server managed by threat actors.
Top 3 Stealer Malware Activity Research
Glupteba
Identified in 2014, Glupteba is a backdoor trojan that downloads infected installers or software exploits via online advertising campaigns that direct users to download software or applications. Once Glupteba is active on a system, botnet operators can deploy additional modules ranging from credential stealers to exploit kits that compromise devices on the target network.
Formbook
Identified in 2016, the developers of Formbook use the malware-as-a-service business model. In this model, malware developers do not distribute the malware themselves but instead sell the malware binary and access to command and control servers. Formbook is designed to steal personal information from victims’ devices and manipulate their devices using control commands from a C2 server. It is designed to collect personal information by using keyloggers and form grabbers to collect victim input along with data from certain software such as browsers, instant messaging, email clients, and FTP clients.
Remcos
Remcos, marketed by Germany-based Breaking Security as legitimate software for remotely managing Windows systems, has been widely used by threat actors in numerous malicious campaigns. It is a sophisticated remote access trojan horse (RAT) that can completely control and monitor any Windows computer running XP or a later version. Threat actors exploit phishing emails to distribute the REMCOS malware via a malicious PDF. The malware makes changes to the registry to ensure persistence on targeted systems.
New Phishing Campaign Detected That Deploying Remcos RAT
Dridex
First identified in 2012, Dridex is a malware that targets its victims’ banking information. Classified as a trojan, the main goal of Dridex is to steal sensitive information such as online banking credentials and financial access. Threat actors are known to distribute the malware to Windows systems via Word and Excel files in phishing email campaigns.
What Should You Know About Ransomware
Conclusion and Mitigations
In the final months of 2021, a security vulnerability called Log4Shell was identified in the Log4J library of Apache, which is used by tens of thousands of organizations. Log4Shell is easily exploitable by threat actors. In the following year, many more critical vulnerabilities were identified. These detected critical security vulnerabilities are frequently used by threat actors to distribute various advanced malware to vulnerable systems and obtain sensitive data. As security solutions have evolved, threat actors have developed malware with advanced capabilities in order to gain access to targeted systems. To protect against security vulnerabilities and advanced malware, it is important to:
- Keep systems and applications up to date by scanning for security vulnerabilities.
- Do not access links in unsafe spam messages or unknown websites.
- Do not provide personal information to untrusted sources.
- Do not rely on e-mails, attachments, files, and links from suspicious or unknown parties.
- Never use USB sticks obtained from unknown sources.
- Use VPN services on public Wi-Fi networks.
- Sensitive data in the system should be backed up at regular intervals.
- Institutions and organizations should provide awareness training to their employees against cyber security threats.
- Up-to-date security solutions should be used in systems and e-mail mail servers.
References
- https://www.malwarebytes.com/emotet
- https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/threats/emotet
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/Dridex-malware
- https://securityscorecard.com/research/detailed-analysis-redline-stealer
- https://nordvpn.com/blog/trickbot/
- https://www.malwarebytes.com/trickbot
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/Dridex-malware
- https://success.trendmicro.com/dcx/s/solution/1123281-remcos-malware-information?language=en_US&sfdcIFrameOrigin=null
- https://www.nozominetworks.com/blog/tracking-malicious-glupteba-activity-through-the-blockchain/
- https://www.fortinet.com/blog/threat-research/deep-analysis-new-formbook-variant-delivered-phishing-campaign-part-I
- https://www.checkpoint.com/cyber-hub/threat-prevention/what-is-malware/what-is-formbook-malware/
- https://purplesec.us/security-insights/top-vulnerabilities-2022/
- https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/topic/spring4shell-vulnerability-details-and-mitigations/
- https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/topic/follina-microsoft-office-code-execution-vulnerability/
- https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/topic/most-dangerous-vulnerabilities-exploited/
- https://www.blumira.com/cve-2022-0609/






